| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Inorganic compounds make up 1%–1.5% of a living cell’s mass. They are small, simple compounds that play important roles in the cell, although they do not form cell structures. Most of the carbon found in organic molecules originates from inorganic carbon sources such as carbon dioxide captured via carbon fixation by microorganisms.
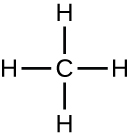
Organic molecules in organisms are generally larger and more complex than inorganic molecules. Their carbon skeletons are held together by covalent bonds. They form the cells of an organism and perform the chemical reactions that facilitate life. All of these molecules, called biomolecule s because they are part of living matter, contain carbon, which is the building block of life. Carbon is a very unique element in that it has four valence electrons in its outer orbitals and can form four single covalent bonds with up to four other atoms at the same time (see Appendix A ). These atoms are usually oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorous, and carbon itself; the simplest organic compound is methane, in which carbon binds only to hydrogen ( [link] ).
As a result of carbon’s unique combination of size and bonding properties, carbon atoms can bind together in large numbers, thus producing a chain or carbon skeleton . The carbon skeleton of organic molecules can be straight, branched, or ring shaped (cyclic). Organic molecules are built on chains of carbon atoms of varying lengths; most are typically very long, which allows for a huge number and variety of compounds. No other element has the ability to form so many different molecules of so many different sizes and shapes.
Molecules with the same atomic makeup but different structural arrangement of atoms are called isomers . The concept of isomerism is very important in chemistry because the structure of a molecule is always directly related to its function. Slight changes in the structural arrangements of atoms in a molecule may lead to very different properties. Chemists represent molecules by their structural formula , which is a graphic representation of the molecular structure, showing how the atoms are arranged. Compounds that have identical molecular formulas but differ in the bonding sequence of the atoms are called structural isomers . The monosaccharides glucose , galactose , and fructose all have the same molecular formula, C 6 H 12 O 6 , but we can see from [link] that the atoms are bonded together differently.

Isomers that differ in the spatial arrangements of atoms are called stereoisomers ; one unique type is enantiomers . The properties of enantiomers were originally discovered by Louis Pasteur in 1848 while using a microscope to analyze crystallized fermentation products of wine. Enantiomers are molecules that have the characteristic of chirality , in which their structures are nonsuperimposable mirror images of each other. Chirality is an important characteristic in many biologically important molecules, as illustrated by the examples of structural differences in the enantiomeric forms of the monosaccharide glucose or the amino acid alanine ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?