| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
L. monocytogenes is generally introduced into food items by contamination with soil or animal manure used as fertilizer. Foods commonly associated with listeriosis include fresh fruits and vegetables, frozen vegetables, processed meats, soft cheeses, and raw milk. US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, “ Listeria Outbreaks,” 2016. Accessed June 29, 2016. https://www.cdc.gov/listeria/outbreaks/index.html. Unlike most other foodborne pathogens, Listeria is able to grow at temperatures between 0 °C and 50 °C, and can therefore continue to grow, even in refrigerated foods.
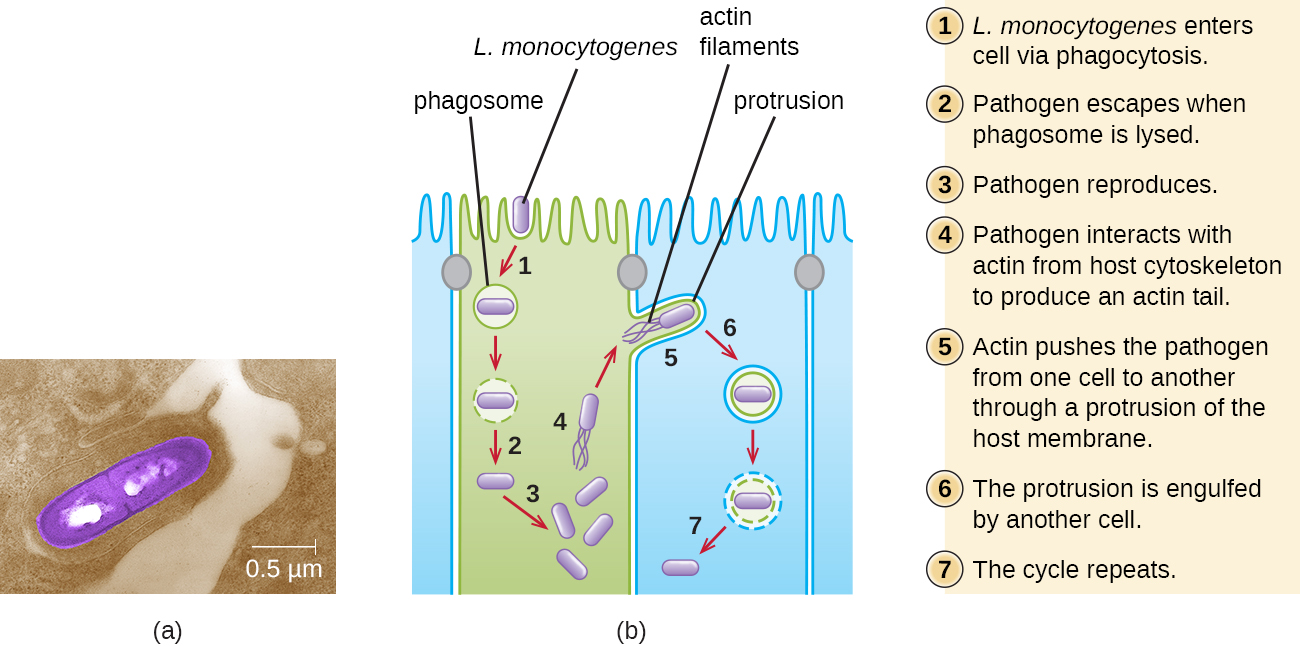
Ingestion of contaminated food leads initially to infection of the gastrointestinal tract. However, L. monocytogenes produces several unique virulence factors that allow it to cross the intestinal barrier and spread to other body systems. Surface proteins called internalins (InlA and InlB) help L. monocytogenes invade nonphagocytic cells and tissues, penetrating the intestinal wall and becoming disseminating through the circulatory and lymphatic systems. Internalins also enable L. monocytogenes to breach other important barriers, including the blood-brain barrier and the placenta. Within tissues, L. monocytogenes uses other proteins called listeriolysin O and ActA to facilitate intercellular movement, allowing the infection to spread from cell to cell ( [link] ).
L. monocytogenes is usually identified by cultivation of samples from a normally sterile site (e.g., blood or CSF ). Recovery of viable organisms can be enhanced using cold enrichment by incubating samples in a broth at 4 °C for a week or more. Distinguishing types and subtypes of L. monocytogenes —an important step for diagnosis and epidemiology—is typically done using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Identification can also be achieved using chemiluminescence DNA probe assays and MALDI-TOF.
Treatment for listeriosis involves antibiotic therapy, most commonly with ampicillin and gentamicin . There is no vaccine available.
Hansen’s disease (also known as leprosy ) is caused by a long, thin, filamentous rod-shaped bacterium Mycobacterium leprae , an obligate intracellular pathogen. M. leprae is classified as gram-positive bacteria, but it is best visualized microscopically with an acid-fast stain and is generally referred to as an acid-fast bacterium . Hansen’s disease affects the PNS, leading to permanent damage and loss of appendages or other body parts.
Hansen’s disease is communicable but not highly contagious; approximately 95% of the human population cannot be easily infected because they have a natural immunity to M. leprae . Person-to-person transmission occurs by inhalation into nasal mucosa or prolonged and repeated contact with infected skin. Armadillos, one of only five mammals susceptible to Hansen’s disease, have also been implicated in transmission of some cases. Sharma, Rahul, Pushpendra Singh, W. J. Loughry, J. Mitchell Lockhart, W. Barry Inman, Malcolm S. Duthie, Maria T. Pena et al., “Zoonotic Leprosy in the Southeastern United States,” Emerging Infectious Diseases 21, no. 12 (2015): 2127-34.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?