| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When samples are prepared for viewing using an SEM, they must also be dehydrated using an ethanol series. However, they must be even drier than is necessary for a TEM. Critical point drying with inert liquid carbon dioxide under pressure is used to displace the water from the specimen. After drying, the specimens are sputter-coated with metal by knocking atoms off of a palladium target, with energetic particles. Sputter-coating prevents specimens from becoming charged by the SEM’s electron beam.
The causative agent of syphilis is Treponema pallidum , a flexible, spiral cell (spirochete) that can be very thin (<0.15 μm) and match the refractive index of the medium, making it difficult to view using brightfield microscopy. Additionally, this species has not been successfully cultured in the laboratory on an artificial medium; therefore, diagnosis depends upon successful identification using microscopic techniques and serology (analysis of body fluids, often looking for antibodies to a pathogen). Since fixation and staining would kill the cells, darkfield microscopy is typically used for observing live specimens and viewing their movements. However, other approaches can also be used. For example, the cells can be thickened with silver particles (in tissue sections) and observed using a light microscope. It is also possible to use fluorescence or electron microscopy to view Treponema ( [link] ).
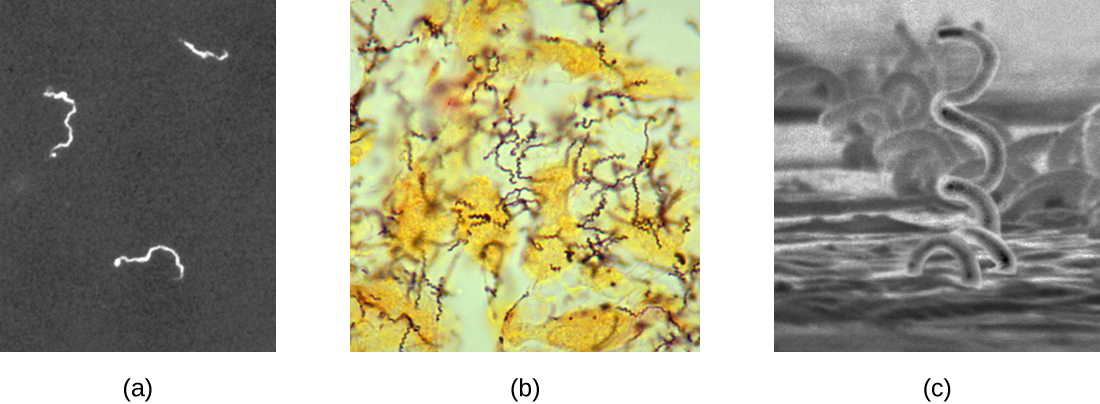
In clinical settings, indirect immunofluorescence is often used to identify Treponema. A primary, unstained antibody attaches directly to the pathogen surface, and secondary antibodies “tagged” with a fluorescent stain attach to the primary antibody. Multiple secondary antibodies can attach to each primary antibody, amplifying the amount of stain attached to each Treponema cell, making them easier to spot ( [link] ).
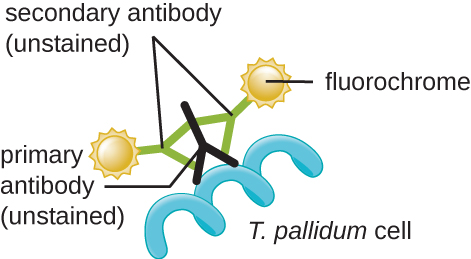
Samples for fluorescence and confocal microscopy are prepared similarly to samples for light microscopy, except that the dyes are fluorochromes. Stains are often diluted in liquid before applying to the slide. Some dyes attach to an antibody to stain specific proteins on specific types of cells ( immunofluorescence ); others may attach to DNA molecules in a process called fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) , causing cells to be stained based on whether they have a specific DNA sequence.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?