| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The complement system is a group of plasma protein mediators that can act as an innate nonspecific defense while also serving to connect innate and adaptive immunity (discussed in the next chapter). The complement system is composed of more than 30 proteins (including C1 through C9) that normally circulate as precursor proteins in blood. These precursor proteins become activated when stimulated or triggered by a variety of factors, including the presence of microorganisms. Complement proteins are considered part of innate nonspecific immunity because they are always present in the blood and tissue fluids, allowing them to be activated quickly. Also, when activated through the alternative pathway (described later in this section), complement proteins target pathogens in a nonspecific manner.
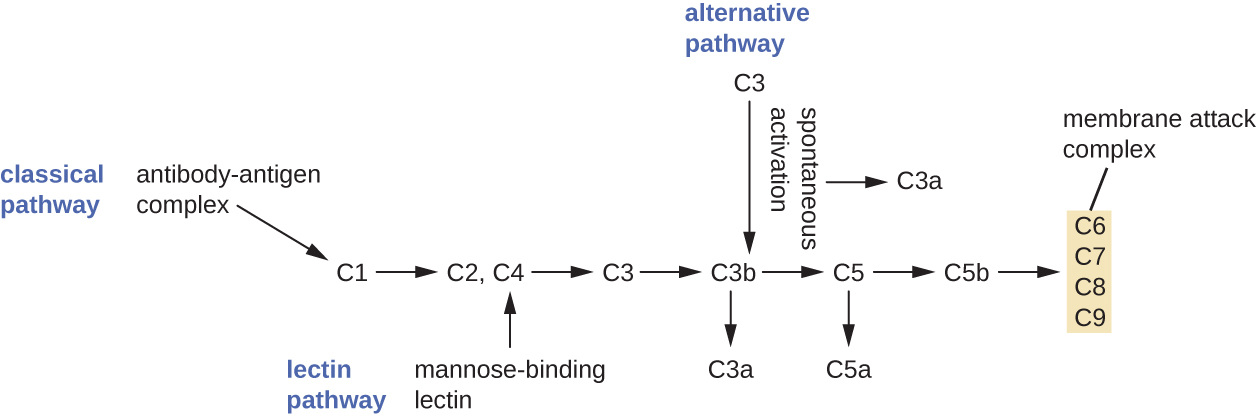
The process by which circulating complement precursors become functional is called complement activation . This process is a cascade that can be triggered by one of three different mechanisms, known as the alternative, classical, and lectin pathways.
The alternative pathway is initiated by the spontaneous activation of the complement protein C3. The hydrolysis of C3 produces two products, C3a and C3b. When no invader microbes are present, C3b is very quickly degraded in a hydrolysis reaction using the water in the blood. However, if invading microbes are present, C3b attaches to the surface of these microbes. Once attached, C3b will recruit other complement proteins in a cascade ( [link] ).
The classical pathway provides a more efficient mechanism of activating the complement cascade, but it depends upon the production of antibodies by the specific adaptive immune defenses. To initiate the classical pathway, a specific antibody must first bind to the pathogen to form an antibody-antigen complex. This activates the first protein in the complement cascade, the C1 complex. The C1 complex is a multipart protein complex, and each component participates in the full activation of the overall complex. Following recruitment and activation of the C1 complex, the remaining classical pathway complement proteins are recruited and activated in a cascading sequence ( [link] ).
The lectin activation pathway is similar to the classical pathway, but it is triggered by the binding of mannose-binding lectin, an acute-phase protein, to carbohydrates on the microbial surface. Like other acute-phase proteins, lectins are produced by liver cells and are commonly upregulated in response to inflammatory signals received by the body during an infection ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?