| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Kayla, a 24-year-old electrical engineer and running enthusiast, just moved from Arizona to New Hampshire to take a new job. On her weekends off, she loves to explore her new surroundings, going for long runs in the pine forests. In July she spent a week hiking through the mountains. In early August, Kayla developed a low fever, headache, and mild muscle aches, and she felt a bit fatigued. Not thinking much of it, she took some ibuprofen to combat her symptoms and vowed to get more rest.
Jump to the next Clinical Focus box.
The science of using living systems to benefit humankind is called biotechnology . Technically speaking, the domestication of plants and animals through farming and breeding practices is a type of biotechnology. However, in a contemporary sense, we associate biotechnology with the direct alteration of an organism’s genetics to achieve desirable traits through the process of genetic engineering . Genetic engineering involves the use of recombinant DNA technology , the process by which a DNA sequence is manipulated in vitro, thus creating recombinant DNA molecule s that have new combinations of genetic material. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism. If the DNA that is introduced comes from a different species, the host organism is now considered to be transgenic .
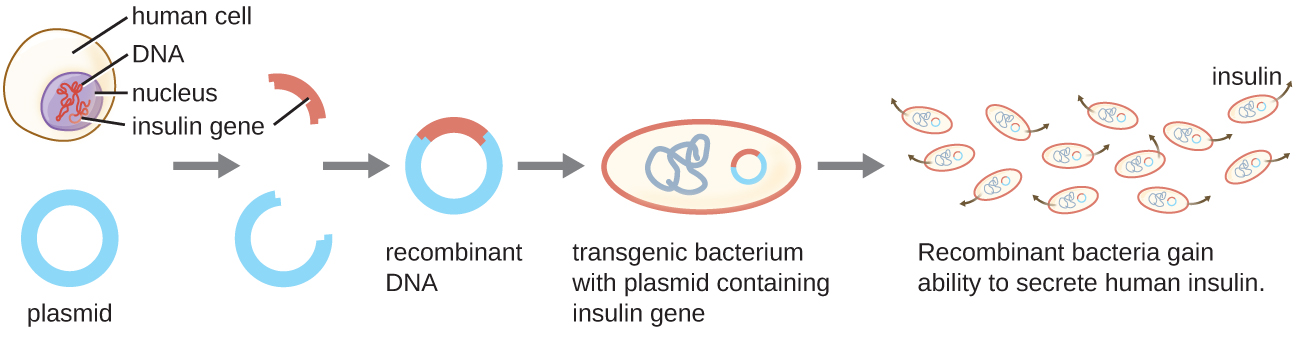
One example of a transgenic microorganism is the bacterial strain that produces human insulin ( [link] ). The insulin gene from humans was inserted into a plasmid. This recombinant DNA plasmid was then inserted into bacteria. As a result, these transgenic microbes are able to produce and secrete human insulin. Many prokaryotes are able to acquire foreign DNA and incorporate functional genes into their own genome through “mating” with other cells ( conjugation ), viral infection ( transduction ), and taking up DNA from the environment ( transformation ). Recall that these mechanisms are examples of horizontal gene transfer —the transfer of genetic material between cells of the same generation.
Herbert Boyer and Stanley Cohen first demonstrated the complete molecular cloning process in 1973 when they successfully cloned genes from the African clawed frog ( Xenopus laevis ) into a bacterial plasmid that was then introduced into the bacterial host Escherichia coli . Molecular cloning is a set of methods used to construct recombinant DNA and incorporate it into a host organism; it makes use of a number of molecular tools that are derived from microorganisms.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?