| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
You know now how small Willy is – about half your size.
Think of all the things you do in your home: in the kitchen, in the lounge, in the bathroom, in the playroom, in the bedroom. Will Willy be able to do them too or will he have problems?
Think of the garden: the games you play, your friends, your pets. Is it safe for Willy? Will he be able to join in your games? Will he be able to play with your friends? What will they think of Willy?
What will Willy think about the way you celebrate your birthday? Your toys? Balloons? Birthday cake with candles? Can you remember how Willy celebrated his birthday? Tell the class.
| LO 1.3.6 | LO 2.1 | LO 2.7 | LO 5.2.1 |
Willy comes to play with me.
I am glad Willy is here.
We play outside on the grass.
We play with the ball.
Willy can run fast.
He can catch the ball.
Well done, Willy.

| LO 3.2.1 | LO 3.3.1 | LO 3.4.3 |
| LO 4.2.1 | LO 4.5.1 | LO 4.6.2 |
| LO 4.1.1 | LO 4.1.2 | LO 4.1.3 |
| LO 3.5.6 |
Learning Outcome 1: LISTENING : The learner is able to listen for information and enjoyment and respond appropriately and critically in a wider range of situations.
Assessment Standard 1.3: We know this when the learner listens with enjoyment to short stories, rhymes, poems and songs from a variety of cultures, and shows understanding:
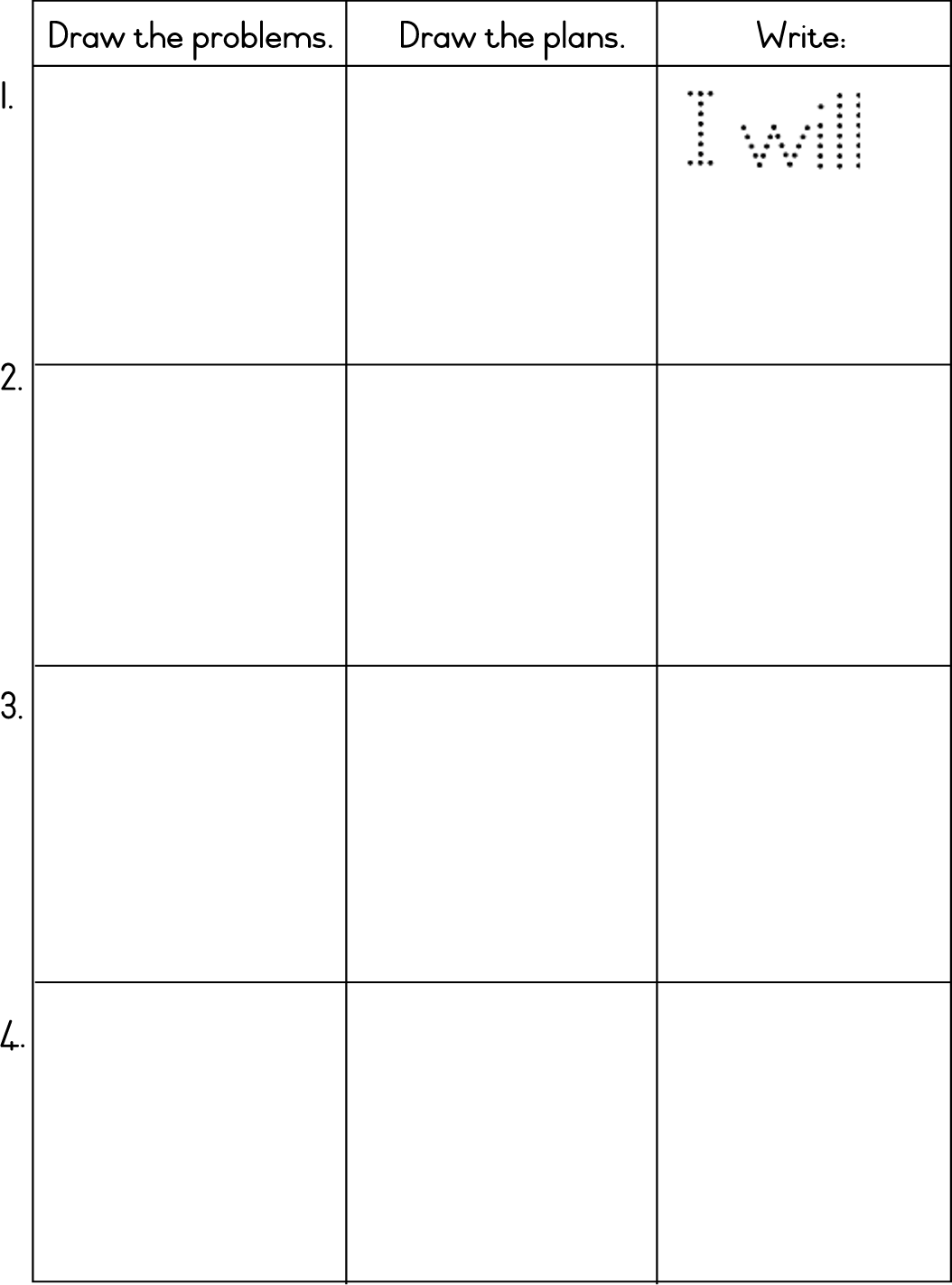
1.3.6 draws a picture of the story, and writes a few words about it;
Assessment Standard 1.4: We know this when the learner listens, enjoys and responds appropriately to riddles and jokes.
Learning Outcome 2: SPEAKING : The learner is able to communicate confidently and effectively in spoken language in a wide range of situations.
Assessment Standard 2.1: We know this when the learner talks about personal experiences, feelings and news;
Assessment Standard 2.7: We know this when the learner tells a familiar short story that has a beginning, middle and ending, using pictures for support if necessary;
Learning Outcome 3: READING AND VIEWING : The learner is able to read and view for information and enjoyment and respond critically to the aesthetic, cultural and emotional values in texts.
Assessment Standard 3.2: We know this when the learner role-plays reading:
3.2.1 holds a book the right way up;
Assessment Standard 3.3: We know this when the learner makes meaning of written text:
3.3.1 reads a story with the teacher and identifies the details;
Assessment Standard 3.4: We know this when the learner recognises letters and words and makes meaning of written text:
3.4.3 uses phonic and word recognition skills to decode new or unfamiliar words in context;
Assessment Standard 3.5: We know this when the learner develops phonic awareness:
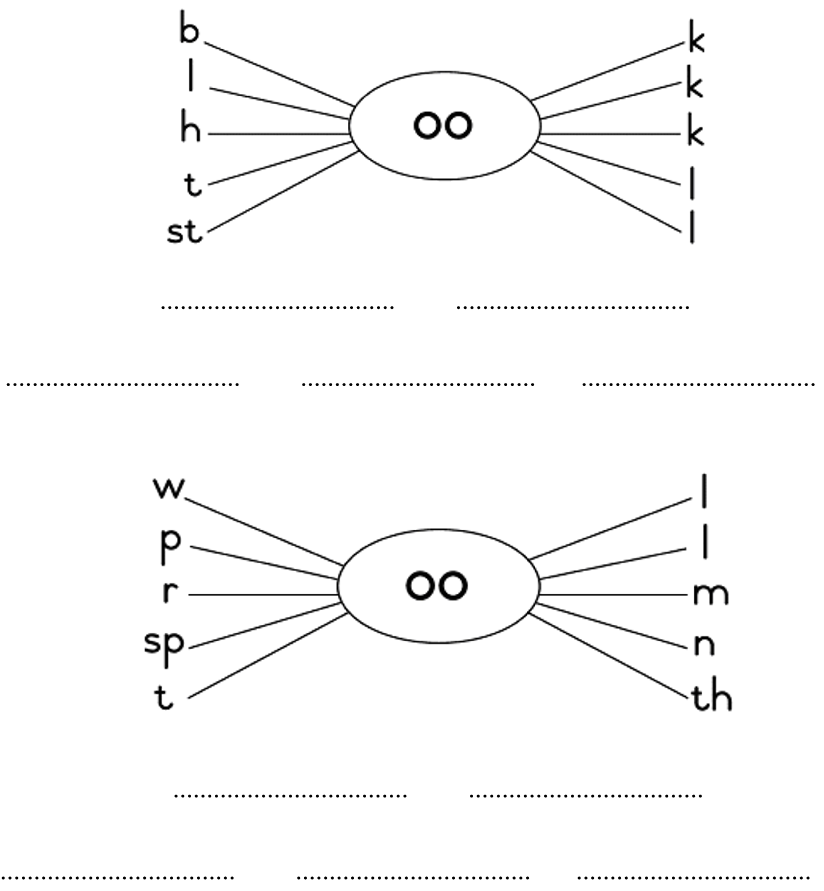
3.5.6 groups common words into word families;
Learning Outcome 4: WRITING : The learner is able to write different kinds of factual and imaginative texts for a wide range of purposes.
Assessment Standard 4.1: We know this when the learner writes with increasing legibility:
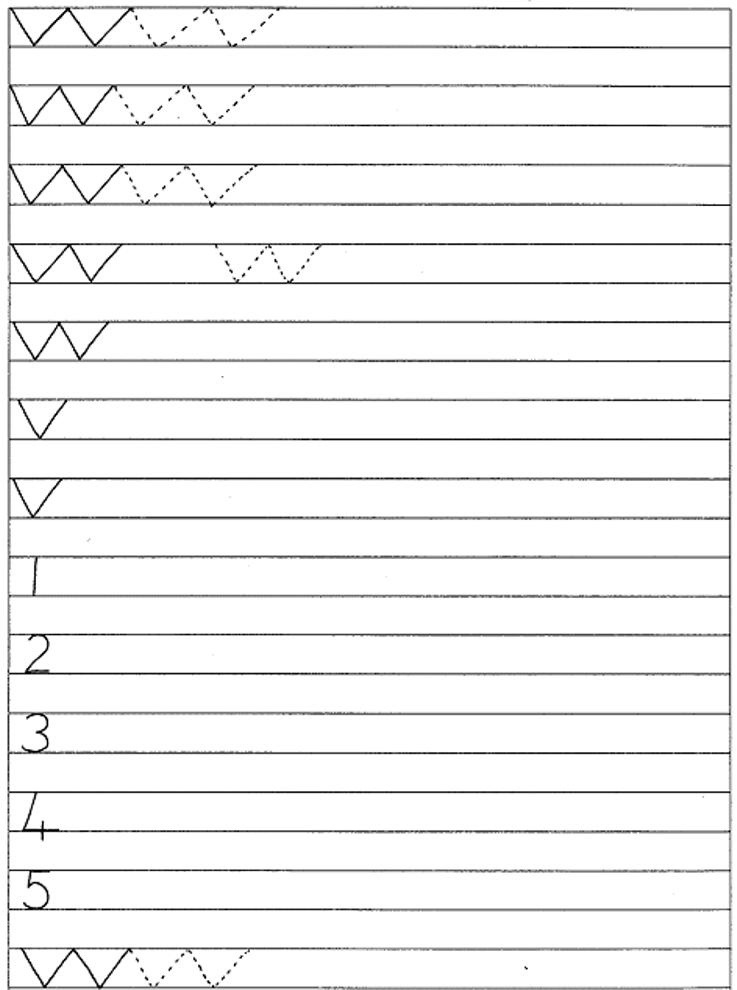
4.1.1 manipulates writing tools like crayons and pencils effectively;
4.1.2 develops letter formation and handwriting skills;
4.1.3 forms letters of the alphabet successfully;
Assessment Standard 4.2: We know this when the learner does pre-writing:
4.2.1 creates and uses drawings as a focus for writing;
Assessment Standard 4.5: We know this when the learner writes so that others can understand, using writing conventions:
4.5.1 uses letters to form single words and short sentences;
Assessment Standard 4.6: We know this when the learner begins to build vocabulary and starts to spell words so that they can be read and understood by others:
4.6.2 spells common words correctly;
Learning Outcome 5: THINKING AND REASONING : The learner is able to use language to think and reason, and access, process and use information for learning.
Assessment Standard 5.2: We know this when the learner uses language to think and reason:
5.2.1 understands and uses language for logic and reasoning, such as cause and effect.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English home language grade 1' conversation and receive update notifications?