| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
There are a few identities relating to the trigonometric functions that make working with triangles easier. These are:
and will be described and applied in this section.
The sine rule applies to any triangle: where is the side opposite , is the side opposite and is the side opposite .
Consider .

The area of can be written as: However, can be calculated in terms of or as:
and
Therefore the area of is:
Similarly, by drawing the perpendicular between point and line we can show that:
Therefore the area of is:
If we divide through by , we get:
This is known as the sine rule and applies to any triangle, right angled or not.
There is a coastline with two lighthouses, one on either side of a beach. The two lighthouses are km apart and one is exactly due east of the other. The lighthouses tell how close a boat is by taking bearings to the boat (remember – a bearing is an angle measured clockwise from north). These bearings are shown. Use the sine rule to calculate how far the boat is from each lighthouse.
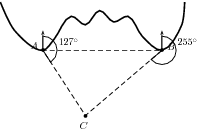
We can see that the two lighthouses and the boat form a triangle. Since we know the distance between the lighthouses and we have two angles we can use trigonometry to find the remaining two sides of the triangle, the distance of the boat from the two lighthouses.
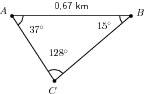
We need to know the lengths of the two sides and . We can use the sine rule to find our missing lengths.
The cosine rule applies to any triangle and states that:
where is the side opposite , is the side opposite and is the side opposite .
The cosine rule relates the length of a side of a triangle to the angle opposite it and the lengths of the other two sides.
Consider which we will use to show that:
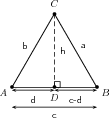
In : from the theorem of Pythagoras.
In : from the theorem of Pythagoras.
We can eliminate from [link] and [link] to get:
In order to eliminate we look at , where we have: So, Substituting this into [link] , we get:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 11 maths' conversation and receive update notifications?