| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
T(t)=K(t) (5.18)

H.5_8: Hệ thống moment- lò xo xoắn.
Nếu lò xo xoắn có mang trước một moment Tp, thì phương trình trên được cải tiến.
T(t) –TP =K(t) (5.19)
c. Ma sát trong chuyển động quay.
Cả ba loại ma sát đã mô tả trong chuyển động tịnh tiến đều có thể áp dụng cho chuyển động quay. Do đó các phương trình (5.13), (5.14) và (5.15) có thể viết lại trong trường hợp này như sau:
(5.20)
T(t)= (Fs)’=0 (5.21)
(5.22)
Trong đó, B :Hệ số ma sát nhớt, moment trên một đơn vị vận tốc góc.
(Fs)=0 là ma sát nghỉ.
Fc : là ma sát coulomb.
Trong vấn đề điều khiển chuyển động, thường khi ta cần đổi một chuyển động quay thành một chuyển động tịnh tiến. Thí dụ,
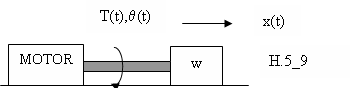
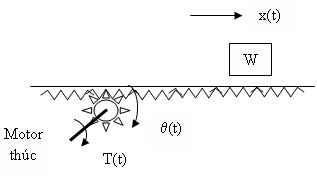
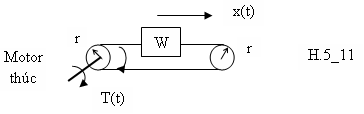
H.5_10
Các hệ thống trên điều có thể được biểu diễn bằng một hệ thống đơn giản với một quán tính tương đương mắc trực tiếp vào một motor thúc.
Thí dụ, khối lượng ở hình H.5_11, có thể xem như là một khối điểm (point mass) chuyển động quanh ròng rọc, bán kính r. Bỏ qua quán tính của ròng rọc, thì quán tính tương đương do motor là: (5.23)
Bây giờ ta xem hệ thống ở hình H.5_9. Gọi L là khoảng di chuyển thẳng của khối lượng khi khoảng cách space convis xoay một vòng. Về nguyên tắc, hai hệ thống ở hình H.5_10 và H.5_11 thì tương đương. Ơû hình H.5_10 khoảng di chuyển thẳng của khối lượng trên mỗi vòng quay của pinion làL=2r.
Do đó, dùng phương trình (5.23) để tính quán tính tương đương của hệ ở hình H.5_9.
(5.24)
Năng lượng và công suất giữ vai trò quan trọng trong việc thiết kế các hệ thống điện cơ.
Năng lượng được tích trữ dưới dạng động năng và thế năng âiãưu khiãøn tính “động” của hệ thống. Tuy nhiên, năng lượng tiêu tán thường ở dạng nhiệt, cũng cần được kiểm soát.
* Khối lượng hoặc quán tính của một vật chỉ khả năng tích trữ động năng. Động năng của một khối lượng di chuyển với vận tốc v là:
(5.25)
Wk: Joule, hoặc Nm ; M: N/m/sec2 ;v: m/s.
đối với một hệ thống quay, động năng được viết:
(5.26)
J: moment quán tính Kg.m2
: vận tốc góc rad/s.
* lò xo tuyến tính bị biến dạng một chiều dài y , sẽ tích trữ một thế năng: (5.27)
* lò xo xoắn, tích trữ thế năng:
(5.28)
: Góc xoắn.
Đối với một bộ phận ma sát, năng lượng biểu diễn một sự mất hoặc tiêu hao bởi hệ thống khi đối kháng với lực ma sát. Công suất tiêu tán trong bộ phận có ma sát là tích số của lực và vận tốc.
P=f.v (5.29)
Vì f= B.v, với B là hệ số ma sát, nên:
P=B.v2 (5.30)
( P: N.m/s2 hoặc watt (w)).
Vậy năng lượng tiêu tán trong bộ phận ma sát la:
(5.31)
Bánh răng, đòn bẩy hoặc dây courroir và pu-li là những cơ phận truyền năng lượng từ một bộ phận này đến một bộ phận khác của hệ thống đễ thay đổi lực, moment, vận tốc và độ dời. Chúng cũng được xem như là những bộ phận phối hợp nhằm đạt đến sự truyền công suất tối đa.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Cơ sở tự động học' conversation and receive update notifications?