| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| LO 1.1.8 | LO 2.1 | LO 3.1.5 | LO 3.5 |
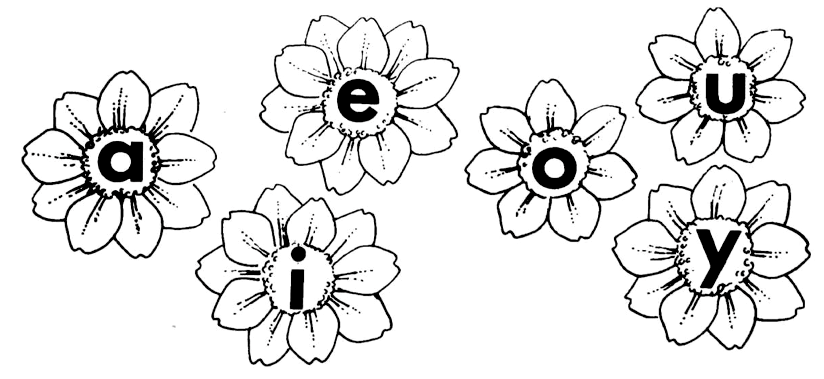
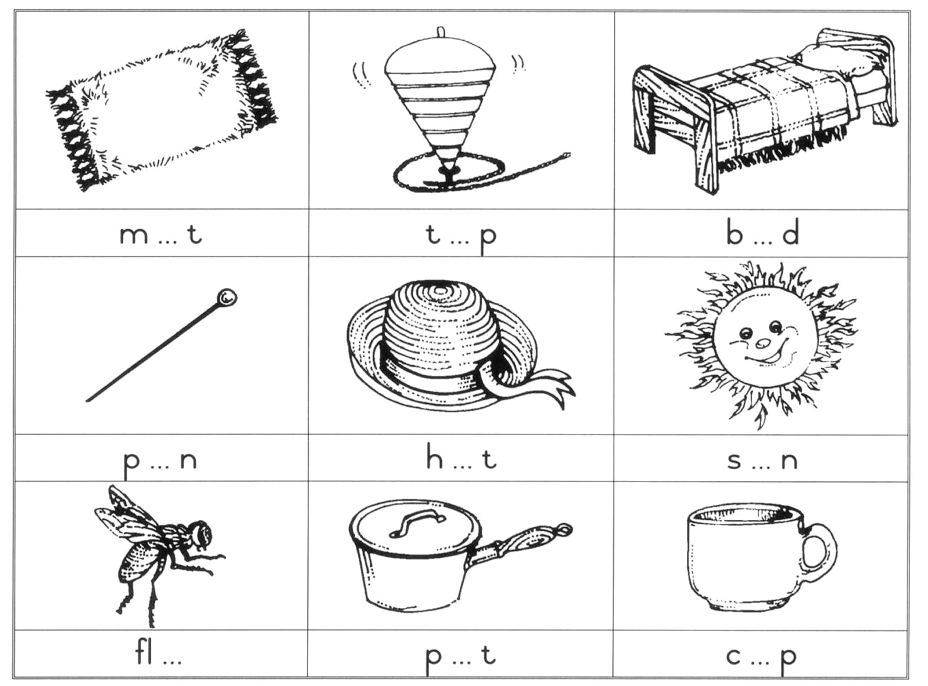
LO 1.4.1 LO 3.4.2 LO 4.7 LO 4.8
| LO 1.1.5 | LO 2.2 | LO 4.7 | LO 4.8 |
The holes in the ground under the hedge began to stir.
Out crept more creepy crawlies of every kind.

Many, many, many ants scurried from their nests deep down in the ground.They followed one another,and off they scurried to find food for their hungry babies.

The wriggly earthworms pushed and pushed until their heads popped out of their tunnels.They could see nice soft, green leaves for their breakfast.

And then something pushed even harder.Out came the blind moles. They pushed and pushed. They sniffed and sniffed looking for their breakfast.
| LO 2.1 | LO 3.2.5 | LO 3.5 | LO 6.4 |
Where were the stick insects?
Where were the chameleons?
Where were the ladybirds?
The branches, leaves and stalks and stems in the hedge began to stir.

The grasshoppers walked along the stalks in the hedge.

The stick insects walked along the stems in the hedge.

The chameleons walked along the branches in the hedge.

The ladybirds walked along the leaves in the hedge.

The caterpillars walked along the leaves in the hedge.
| LO 1.2 | LO 2.6 | LO 3.1.5 | LO 3.2.4 |
1. I’m long and hairy.I eat green leaves.
2. I have wings.I can fly.I live in a hive.
3. Sammy will not catch me.I can hop, hop, hop up high.
4. I’m long and thin.I live under the ground.
5. I spin my web to catch my breakfast.
| LO 1.2 | LO 3.2.4 |
The frogs left their holes in the tree trunk in the hedge.
They stretched their legs and hopped to the pond.
The birds left their nests in the hedge.
They spread their wings and flew off.
The bees left their hives in the hedge.
They spread their wings and flew off to the garden to collect the nectar from the flowers.
The butterflies left their homes in the hedge.
They spread their wings and flew off to the garden to collect the nectar from the flowers.
It’s breakfast time on the farm!
1. What do you think Sammy Snake had for breakfast?
2. What do you think the snails had for breakfast?
3. What do you think the chameleons had for breakfast?
4. What do you think the birds had for breakfast?
| LO 1.1.5 | LO 1.1.7 | LO 2.6 | LO 3.5 |

..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
| LO 2.5 | LO 3.1.5 | LO 4.6 | LO 4.8 |
Learning Outcome 1: LISTENING : The learner is able to listen for information and enjoyment and respond appropriately and critically in a wider range of situations.
Assessment Standard 1.1: We know this when the learner understands short, simple stories:
1.1.5 answers simple, literal yes/no questions with short answers;
1.1.7 answers questions that connect the story to own life in own home language;
1.1.8 shows understanding of recounts by recalling the events in sequence;
Assessment Standard 1.2: We know this when the learner shows understanding of a simple description by identifying what is described;
Assessment Standard 1.5: We know this when the learner shows respect for classmates by giving them a chance to speak, listening to them and encouraging their attempts to speak their additional language;
Learning Outcome 2: SPEAKING : The learner is able to communicate confidently and effectively in spoken language in a wide range of situations.
Assessment Standard 2.1: We know this when the learner responds appropriately to simple questions;
Assessment Standard 2.2: We know this when the learner memorises and performs songs, action rhymes and simple poems;
Assessment Standard 2.5: We know this when the learner talks about a picture or drawings;
Assessment Standard 2.6: We know this when the learner attends to pronunciation as part of reading;
Learning Outcome 3: READING AND VIEWING : The learner is able to read and view for information and enjoyment, and respond critically to the aesthetic, cultural and emotional values in texts;
Assessment Standard 3.1: We know this when the learner uses pictures to understand written texts:
3.1.5 draws a picture to illustrate a sentence;
Assessment Standard 3.2: We know this when the learner begins to make meaning of written text by reading with the teacher:
3.2.4 answers short questions about the story;
3.2.5 retells the story;
Assessment Standard 3.5: We know this when the learner reads fiction and non-fiction books at an appropriate level for information and enjoyment;
Learning Outcome 4: WRITING : The learner is able to write different kinds of factual and imaginative texts for a wide range of purposes.
Assessment Standard 4.6: We know this when the learner uses punctuation – capital letters and full stops;
Assessment Standard 4.7: We know this when the learner uses uses phonic knowledge to begin to spell correctly;
Assessment Standard 4.8: We know this when the learner uses spells familiar words correctly;
Learning Outcome 6: GRAMMAR AND VOCABULARY : The learner knows and is able to use the sounds, vocabulary and grammar of the language to create and interpret texts.
Assessment Standard 6.4: We know this when the learner understands and uses some adjectives.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English first additional language grade 2' conversation and receive update notifications?