| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Chlorine forms a series of oxides ( [link] ) in which the chlorine has the formal oxidation states +1, +4, +6, and +7. The physical properties of the oxides are summarized in [link] . While, the oxides of chlorine are not very stable (in fact several are shock sensitive and are prone to explode) the conjugate oxyacids are stable.
| Compound | Mp (°C) | Bp (°C) |
| Cl 2 O | -116 | 4 |
| ClO 2 | -5.9 | 10 |
| Cl 2 O 4 | -117 | 44.5 |
| Cl 2 O 6 | 3.5 | unstable |
| Cl 2 O 7 | -91.5 | 82 |
Dichlorine monoxide (Cl 2 O, [link] a) is a yellowish-red gas that is prepared by the reaction of chlorine with mercury oxide, [link] , or with a solution of chlorine in CCl 4 .

When heated or subject to a spark, Cl 2 O explodes to Cl 2 and O 2 . Dichlorine monoxide reacts with water to form an orange-yellow solution of hypochlorous acid, [link] .
Chlorine dioxide (ClO 2 ) is a yellowish gas at room temperature and is commonly used in industry as an oxidizing agent. The best synthesis of ClO 2 involves the reduction of potassium chlorate (KClO 3 ) by oxalic acid at 90 °C, since the CO 2 formed acts as a diluent for the highly explosive ClO 2 . On an industrial scale ClO 2 is made by the exothermic reaction of sodium chlorate with SO 2 in sulfuric acid, [link] . The photolysis of ClO 2 yields a dark brown solid with the formula Cl 2 O 3 ; however, its facile explosive decomposition precludes study.
The structure of ClO 2 ( [link] b) is equivalent to SO 2 with one extra electron, resulting in a paramagnetic unpaired electron species. Unusually, despite the unpaired electron configuration, ClO 2 shows no tendency to dimerize. This is unlike the analogous NO 2 molecule.
Dichlorine tetraoxide (Cl 2 O 4 ) is commonly called chlorine perchlorate as a consequence of its structure ( [link] c). Dichlorine hexaoxide (Cl 2 O 6 ) is an unstable red oil that has the ionic structure in the solid state: [ClO 2 ] + [ClO 4 ] - .
Dichlorine heptoxide (Cl 2 O 7 ) is a relatively stable oil, that is prepared by the dehydration of perchloric acid at -10 °C, [link] , followed by vacuum distillation. The structure of Cl 2 O 7 ( [link] d) has been determined by gas phase electron diffraction.

The reaction of Cl 2 O 7 with alcohols and amines yields alkyl perchlorates (ROClO 3 ) and amine perchlorates (R 2 NClO 3 ), respectively.
Given the isolobal relationship between the halogens it is not surprising that the mixed dihalogens can be prepared, e.g., ClF, ICl, and BrCl. Chlorine fluoride is a highly reactive gas (Bp = -100.1 °C) that is a powerful fluorinating agent, and is prepared by the oxidation of chlorine by chlorine trifluoride, [link] .
The higher electronegativity of fluorine as compared to chlorine ( [link] ), and the ability of chlorine to form more than one bond, means that higher fluorides of chlorine are also known, i.e., ClF 3 and ClF 5 . Chlorine trifluoride (CF 3 , Bp = 11.75 °C) is a useful fluorinating agent, that is prepared by the high temperature reaction of elemental chlorine and fluorine, is a useful fluorinating age. The gaseous pentafluoride (ClF 5 , Bp = -31.1 °C) is prepared by the reaction of potassium chloride with fluorine, [link] .
The structure of ClF 3 is T-shaped with two lone pairs on chlorine ( [link] a), while that of ClF 5 is square pyramidal with a single lone pair on chlorine ( [link] b).
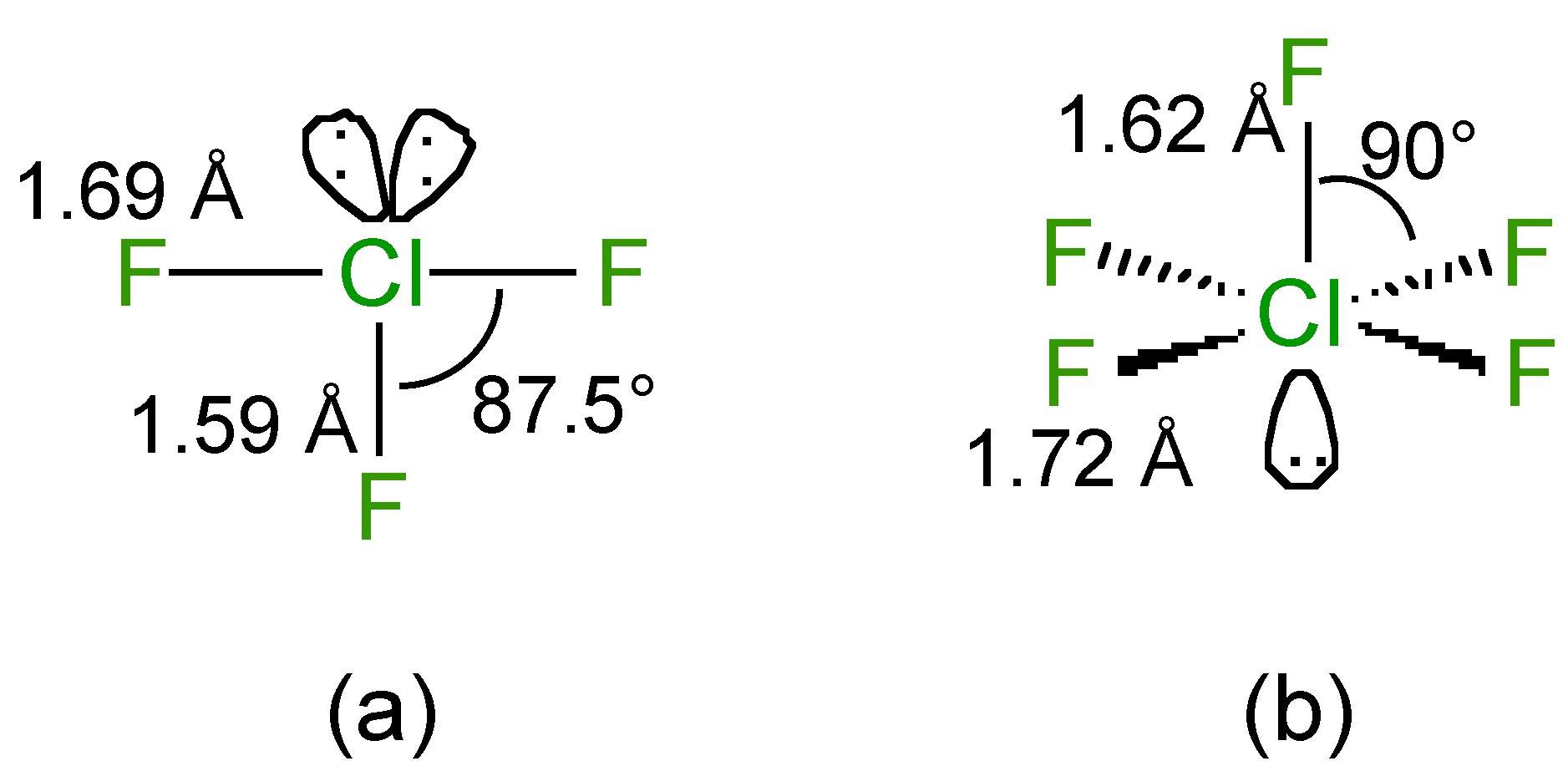
In general the halogen fluorides are very reactive; explosive reactions occur with organic compounds. They are all powerful fluorinating agents when diluted with nitrogen, and the order of reactivity follows:
Like most halogen fluorides, ClF, ClF 3 and ClF 5 all react with strong bases (e.g., alkali metal fluorides) to form anions, [link] and [link] , and strong acids (e.g., AsF 5 and SbF 5 ) to form cations, [link] , [link] , and [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry of the main group elements' conversation and receive update notifications?