| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
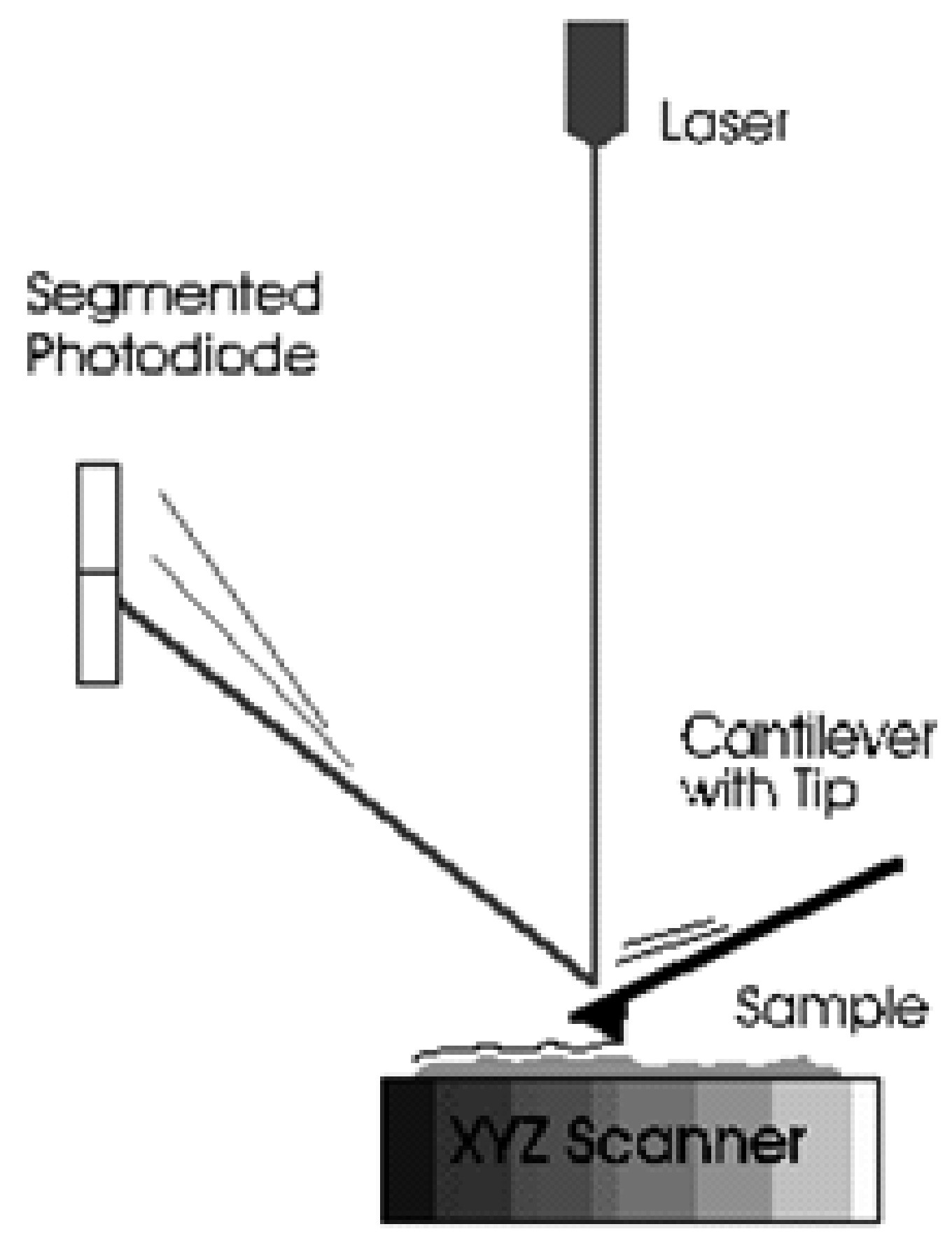
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a high-resolution form of scanning probe microscopy, also known as scanning force microscopy (SFM). The instrument uses a cantilever with a sharp tip at the end to scan over the sample surface ( [link] ). As the probe scans over the sample surface, attractive or repulsive forces between the tip and sample, usually in the form of van der Waal forces but also can be a number of others such as electrostatic and hydrophobic/hydrophilic, cause a deflection of the cantilever. The deflection is measured by a laser ( [link] ) which is reflected off the cantilever into photodiodes. As one of the photodiodes collects more light, it creates an output signal that is processed and provides information about the vertical bending of the cantilever. This data is then sent to a scanner that controls the height of the probe as it moves across the surface. The variance in height applied by the scanner can then be used to produce a three-dimensional topographical representation of the sample.
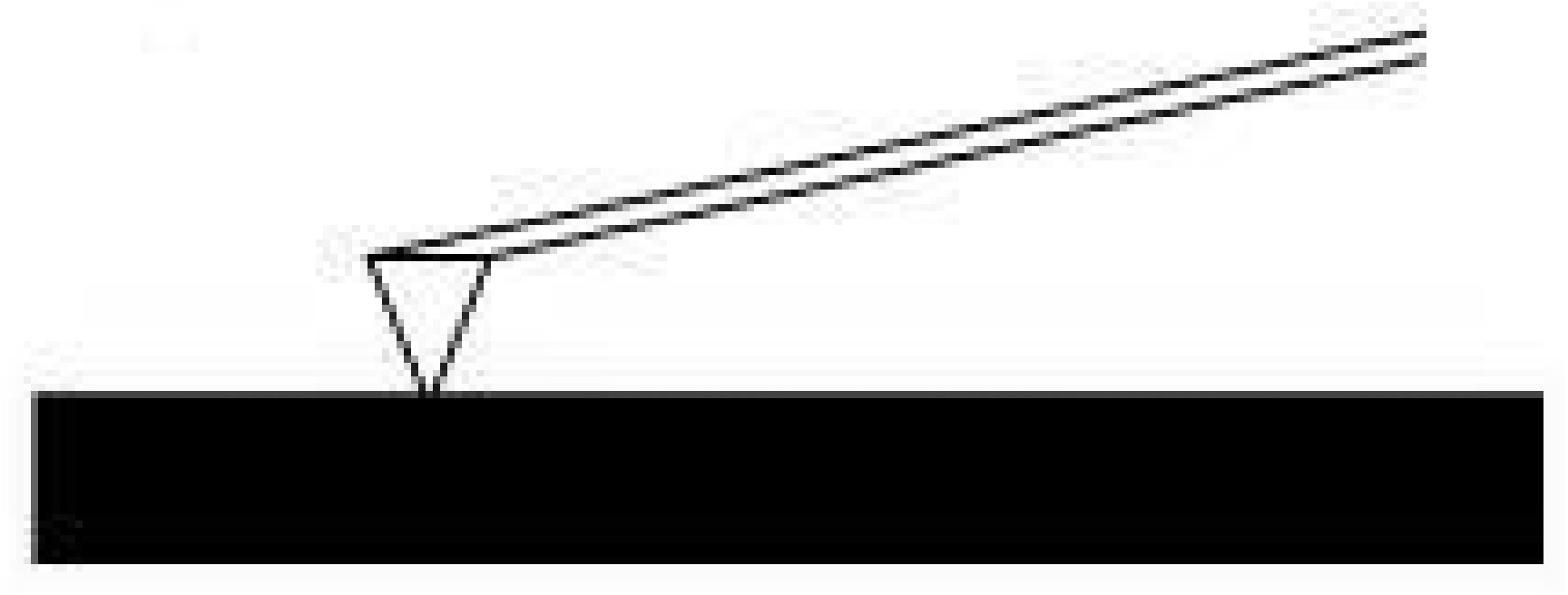
The contact mode method utilizes a constant force for tip-sample interactions by maintaining a constant tip deflection ( [link] .). The tip communicates the nature of the interactions that the probe is having at the surface via feedback loops and the scanner moves the entire probe in order to maintain the original deflection of the cantilever. The constant force is calculated and maintained by using Hooke's Law, [link] . This equation relates the force (F), spring constant (k), and cantilever deflection (x). Force constants typically range from 0.01 to 1.0 N/m. Contact mode usually has the fastest scanning times but can deform the sample surface. It is also only the only mode that can attain "atomic resolution."
In the tapping mode the cantilever is externally oscillated at its fundamental resonance frequency ( [link] ). A piezoelectric on top of the cantilever is used to adjust the amplitude of oscillation as the probe scans across the surface. The deviations in the oscillation frequency or amplitude due to interactions between the probe and surface are measured, and provide information about the surface or types of material present in the sample. This method is gentler than contact AFM since the tip is not dragged across the surface, but it does require longer scanning times. It also tends to provide higher lateral resolution than contact AFM.
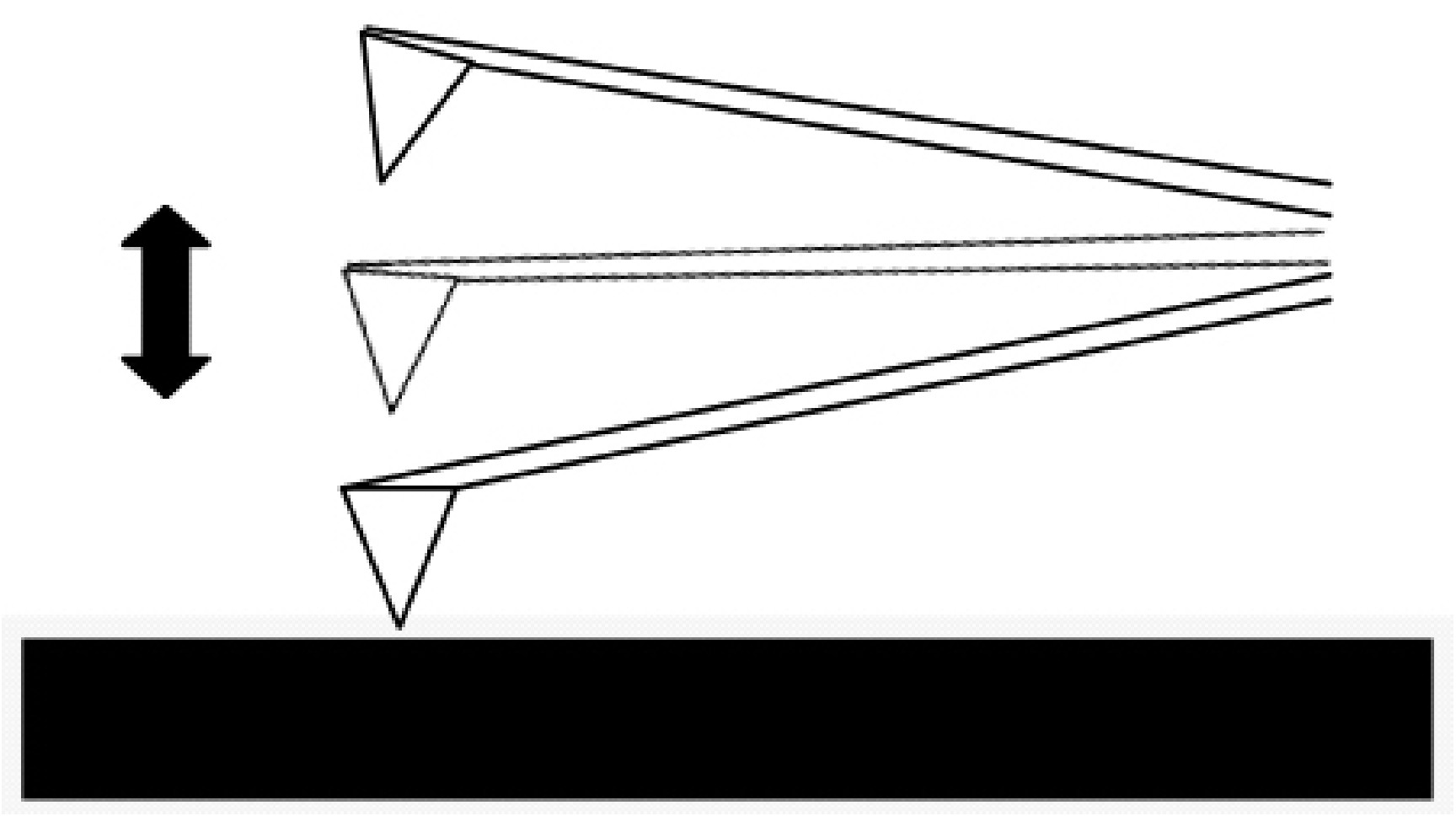
For noncontact mode the cantilever is oscillated just above its resonance frequency and this frequency is decreased as the tip approaches the surface and experiences the forces associated with the material ( [link] ). The average tip-to-sample distance is measured as the oscillation frequency or amplitude is kept constant, which then can be used to image the surface. This method exerts very little force on the sample, which extends the lifetime of the tip. However, it usually does not provide very good resolution unless placed under a strong vacuum.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Carbon nanotubes' conversation and receive update notifications?