| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Boumateriale
Wanneer ‘n huis gebou word, word materiale gebruik wat natuurlik is of wat gemaak moes word. Hier is ‘n prentjie van ‘n huisie. Kleur die natuurlike materiale geel in en die ander materiale rooi.
Hout
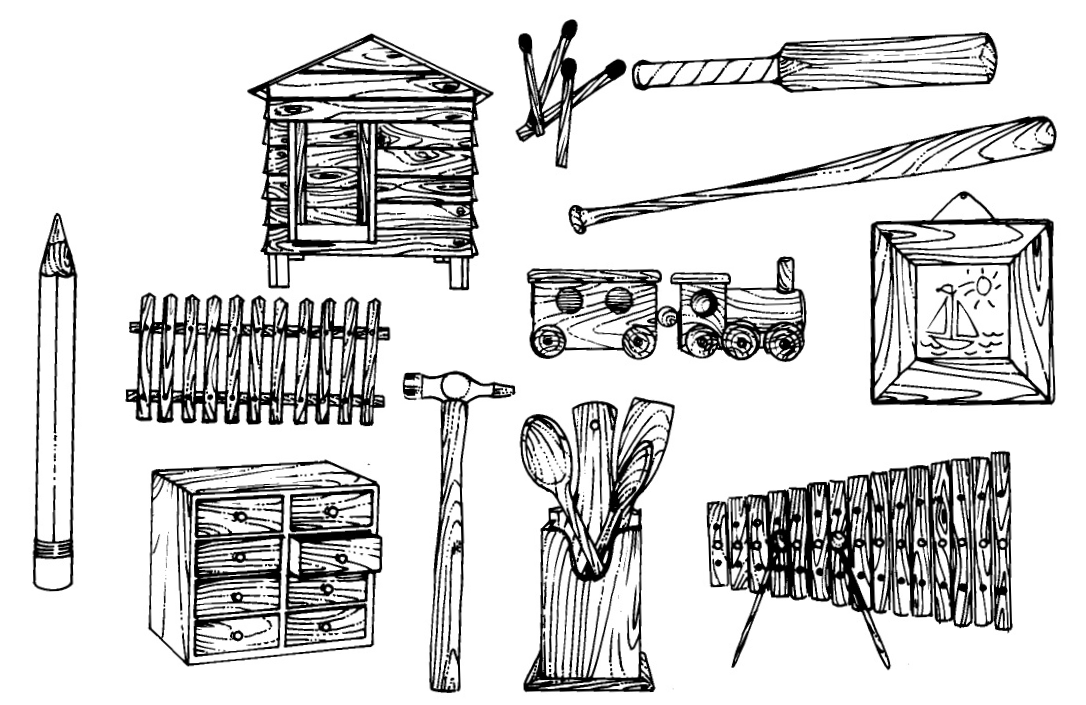
Een van die natuurlike produkte wat gebruik is om die huisie te bou, is hout.
Hout is ‘n wonderlike hulpbron vir die mens. Deel die klas in ses groepe. Gee drie minute kans om alles te lys wat van hout gemaak is in die:
klas
jou kamer by die huis
jou sitkamer by die huis
die kombuis
op die skoolterrein
I
in die skoolsaal
1. Watter gevolgtrekking kan jy hieruit maak?
My gevolgtrekking is: ____________________________
Bakstene

Om mee te skryf
Duisende jare gelede het mense allerhande maniere gebruik om te skryf. Hulle het materiale van dierprodukte, klippe, plante en klei gebruik. Hulle het op papirus, bas, dierevelle en rotse geskryf en tekeninge gemaak.
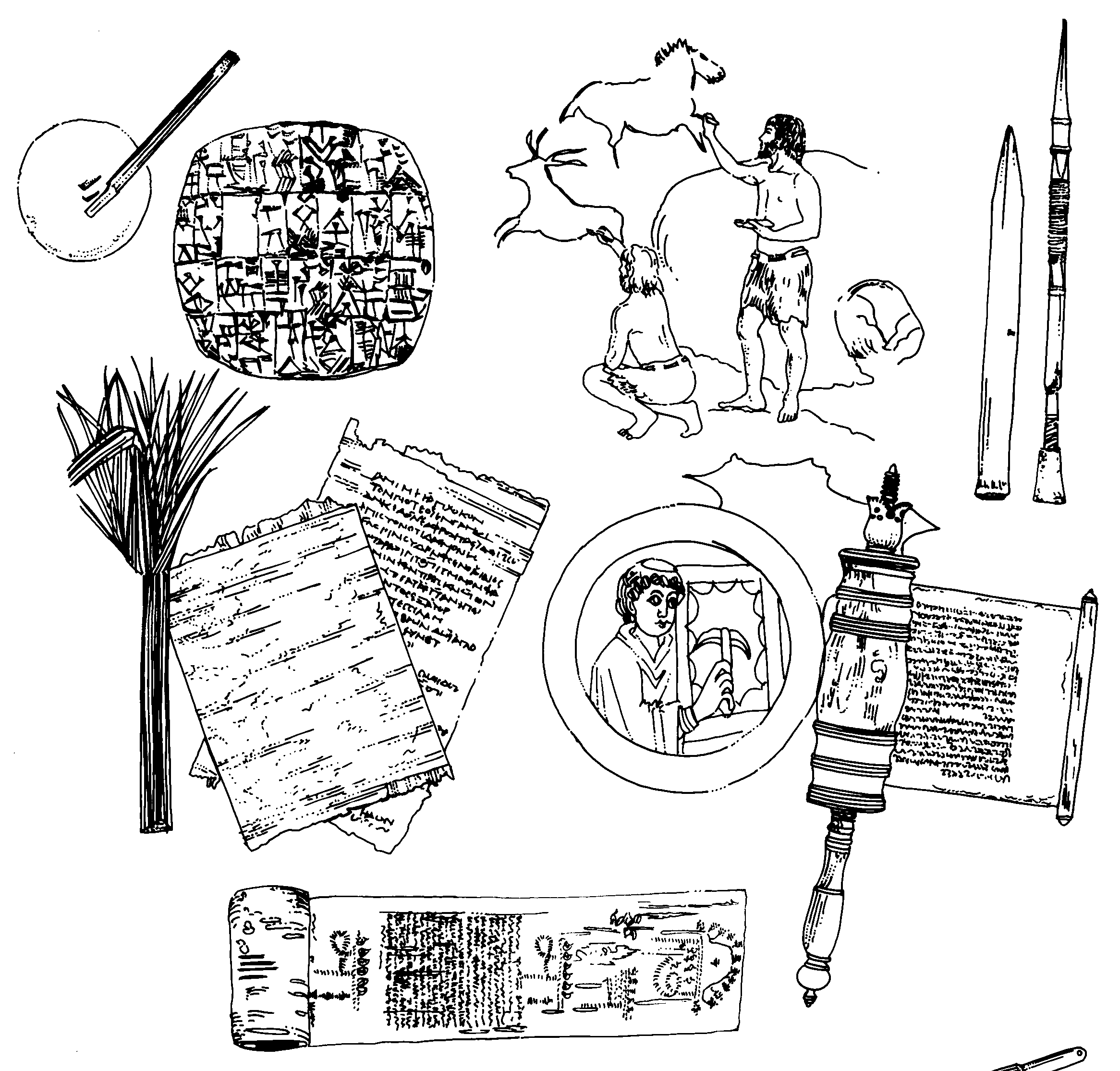
Vandag is dit baie makliker. Ons gaan net eenvoudig winkels toe en koop die wonderlikste skryfgoed wat ons wil hê. Al hierdie goed word van verskillende soorte materie gemaak.
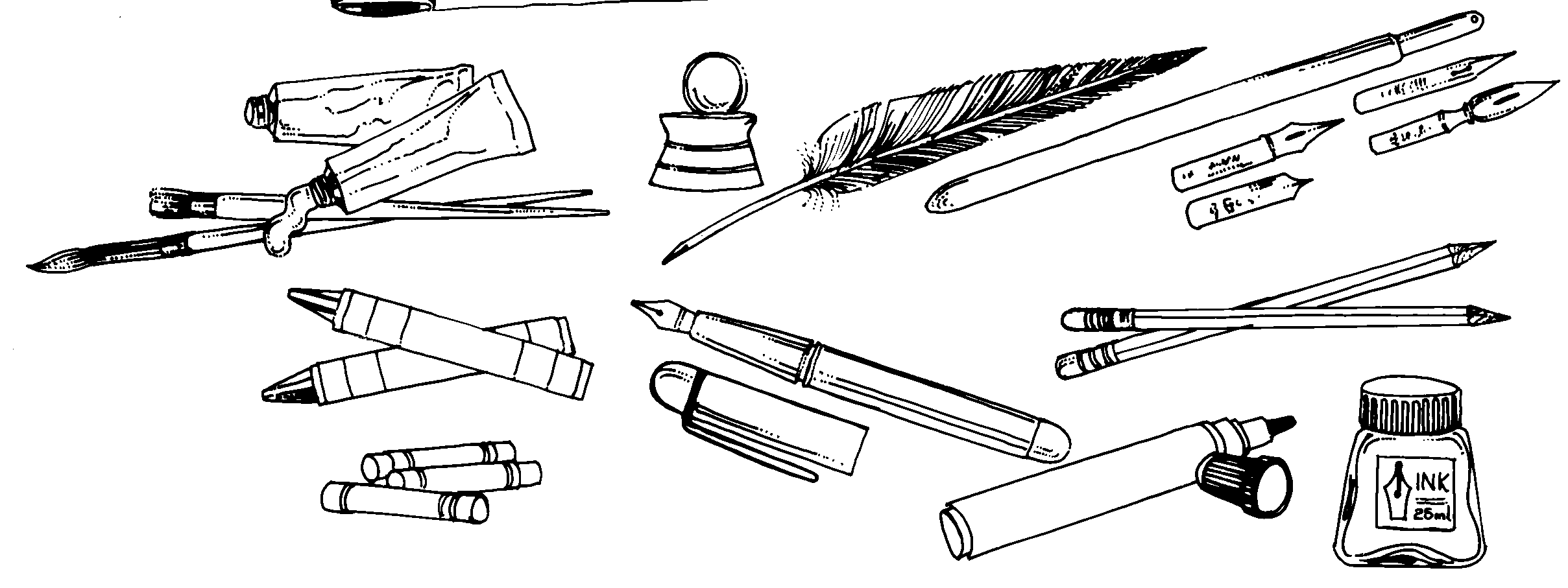
Dink aan iemand uit ons verre verlede wat jou nog altyd gefassineer het. Stuur ‘n kort SMS-boodskap aan hom/haar om te bewys hoe die tegnologie oor ‘skryf’ deur die jare verander het.
LEERUITKOMS 1: WETENSKAPLIKE ONDERSOEK
Die l eerder is in staat om met selfvertroue op weetgierigheid oor natuurlike verskynsels te reageer, en om binne die konteks van wetenskap, tegnologie en die omgewing verbande te ondersoek en probleme op te los.
Assesseringstandaard
Dis duidelik wanneer die leerder
1.2 ondersoeke uitvoer en data versamel, bv.:
1.2.1 merk ooglopende veranderings of interessante besonderhede op en lewer kommentaar daarop.
LEERUITKOMS 2: KONSTRUKSIE VAN WETENSKAPKENNIS Die leerder ken, interpreteer en pas wetenskaplike, tegnologiese en omgewings- kennis toe.
Assesseringstandaard
Dis duidelik wanneer die leerder
2.2 inligting kategoriseer, bv.:
2.2.1 volg instruksies om diere in groepe van dié met twee bene, met vier bene en met meer as vier bene te sorteer.
LEERUITKOMS 3: WETENSKAP, DIE SAMELEWING EN DIE OMGEWING Die leerder is in staat om begrip van die onderlinge verband tussen wetenskap en tegnologie, die samelewing en die omgewing te toon .
Assesseringstandaard
Dis duidelik wanneer die leerder
3.2 die impak van wetenskap en tegnologie verstaan.
Boumateriale:
Om mee te skryf:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natuurwetenskappe graad 4' conversation and receive update notifications?