| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
f(t)-T= Ky(t)(5.12)
Mỗi khi có sự chuyển động hoặc khuynh hướng chuyển động giữa hai vật, lực ma sát sẽ xuất hiện. Lực ma sát gặp trong các hệ vật lý thường là phi tuyến. Những đặc tính của các loại lực ma sát giữa hai bề mặt tiếp xúc thường phụ thuộc vào các hệ số như là sự phối hợp bề mặt, áp suất giữa các bề mặt, vận tốc tương đối của chúng và những thứ khác, làm cho việc mô tả toán học một cách chính xác lực ma sát thì rất khó. Tuy nhiên, với chủ đích thực hành, lực ma sát có thể chia thành ba loại như sau: Ma sát trượt, ma sát nghĩ và ma sát coulomb.
Ma sát trượt biểu diễn một lực cản có liên hệ tuyến tính giữa lực tác dụng và vận tốc. Lực ma sát trượt thường được mô hình hoá bằng một dashpot (ống đệm), có ký hiệu như hình H.5_5.
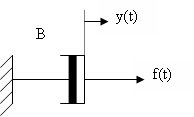
Hình H.5_5: Dashpot của ma sát trượt.
Phương trình biểu diễn lực ma sát trượt:
(5.13)
Trong đó: B là hệ số ma sát trượt. (N/m/sec)
Hình H.5_5a, trình bày sự tương quan giữa lực ma sát trượt và vận tốc.
Ma sát nghĩ biểu diễn một lực cản, có khuynh hướng ngăn cản chuyển động lúc vừa bắt đầu (khi chuyển động bắt đầu ma sát nghĩ có trị cực đại bằng ma sát trượt). Ma sát nghĩ được biểu diễn bởi biễu thức:
f(t) = (Fs)y’=0 (5.14)
Trong đó: (Fs)y’ = 0 được định nghĩa như là lực ma sát nghĩ tồn tại chỉ khi vật đứng yên nhưng đang có khuynh hướng chuyển động. Dấu của lực tùy thuộc và chiều chuyển động hoặc chiều ban đầu của vận tốc. Sự tương quan giữa lực và vận tốc vẽ ở hình H.5_5b. Nhớ là một khi chuyển động bắt đầu, lực ma sát nghĩ biến mất, và loại lực ma sát khác xuất hiện.
Lực ma sát coulomb là một lực cản, có độ lớn không đổi đối với sự biến thiên của vận tốc. Dấu của lực thì thay đổi khi vận tốc đổi chiều. Phương trình toán học của lực ma sát coulomb:
(5.15)
Trong đó Fc là hệ số ma sát coulomb. Sự tương quan giữa lực và vận tốc vẽ ở hình H.5_5c.

H.5_5a. H.5_5b. H.5_5c.
Chuyển động quay của một vật có thể được định nghĩa như là chuyển động của vật quanh một trục cố định. Các biến số thường dùng để mô tả chuyển động quay là moment; gia tốc góc ; vận tốc góc ; và góc dời .
Các bộ phạân sau đây thường được đưa vào để mô hình hoá chuyển động quay.
Quán tính J, được xem như là chỉ thị tính chất của một bộ phận tích trữ động năng trong chuyển động quay. Quán tính của vật phụ thuộc vào sự tổng hợp hình học quanh trục quay và khối lượng của nó. J còn gọi là moment quán tính.
Thí dụ: quán tính của một dĩa tròn hoặc một trục tròn quay quanh trục hình học là:
(5.16)
Trong đó, M là khối lượng của dĩa hoặc của trục và r là bán kính của chúng.
Khi một moment được áp dụng vào một cố thể với quán tính J, như hình H.5_7, thì phương trình moment được viết:
T(x)= (5.17)
J : Kg.m2 ; T :N.m ; :radian.
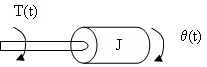
H.5_7: Hệ thống moment _quán tính.
b. Lò xo xoắn (torsional spring).
Khi áp dụng một moment lên một thanh hay một trục quay có khối lượng không đáng kể, trục quay một góc . Nếu k là hằng số xoắn, moment trên một đơn vị góc dời, thì hệ thống có thể biểu diễn bằng hình H.5_8 và phương trình:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Cơ sở tự động học' conversation and receive update notifications?