| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The final method of expressing direction is to use a bearing . A bearing is a direction relative to a fixed point.
Given just an angle, the convention is to define the angle with respect to the North. So, a vector with a direction of has been rotated clockwise relative to the North. A bearing is always written as a three digit number, for example or (for ).
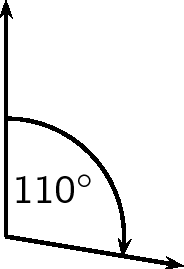
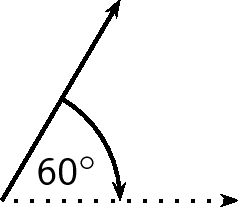
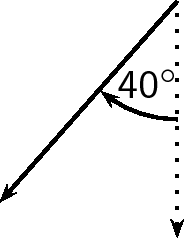
In order to draw a vector accurately we must specify a scale and include a reference direction in the diagram. A scale allows us totranslate the length of the arrow into the vector's magnitude. For instance if one chose a scale of 1 cm = 2 N (1 cm represents 2 N), aforce of 20 N towards the East would be represented as an arrow 10 cm long. A reference direction may be a line representing a horizontal surface or the points of a compass.

Method: Drawing Vectors
Represent the following vector quantities:
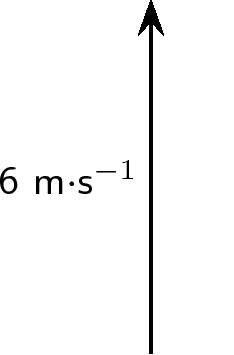

Draw each of the following vectors to scale. Indicate the scale that you have used:
Vectors are mathematical objects and we need to understand the mathematical properties of vectors, like adding and subtracting.
For all the examples in this section, we will use displacement as our vector quantity. Displacement was discussed in Grade 10.
Displacement is defined as the distance together with direction of the straight line joining a final point to an initial point.
Remember that displacement is just one example of a vector. We could just as well have decided to use forces or velocities to illustrate the properties of vectors.
When vectors are added, we need to add both a magnitude and a direction. For example, take 2 steps in the forward direction, stop and then take another 3 steps in the forward direction. The first 2 steps is a displacement vector and the second 3 steps is also a displacement vector. If we did not stop after the first 2 steps, we would have taken 5 steps in the forward direction in total. Therefore, if we add the displacement vectors for 2 steps and 3 steps, we should get a total of 5 steps in the forward direction. Graphically, this can be seen by first following the first vector two steps forward and then following the second one three steps forward (ie. in the same direction):

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics - grade 10 [caps 2011]' conversation and receive update notifications?