| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Mr Mole and the Wise Old Owl also arrived with their wishes. Willy loves to have his friends with him. They play hide and seek, Blind Man’s Buff and laugh and play the whole day. They are so tired and now they have to go home.
Before he closes his eyes Willy also makes a wish. “I wish that every day will be as happy as this one was,” he said.
Three Wishes
I wish, I wish that I could be
A little bird up in the tree.
I’d look for the tiniest little mouse.
And find the path to Willy’s tree house.
I wish, I wish that I could go
On the underground of Mr Mole.
I’d wave to all as we go past,
Like a roller coaster we’d go so fast.
I wish, I wish that Willy could be
Here in my house and play with me.
We’d visit the zoo and the city park too
And he’d teach me all the things he can do!
Things to do:
| LO 1.1 | LO 1.3 | ||
| LO 2.8 | LO 5.1.2 |

| LO 1.1 | LO 1.2 | ||
| LO 2.8 | LO 2.8.3 |
| LO 4.1.1 | LO 4.1.2 | LO 4.1.3 |
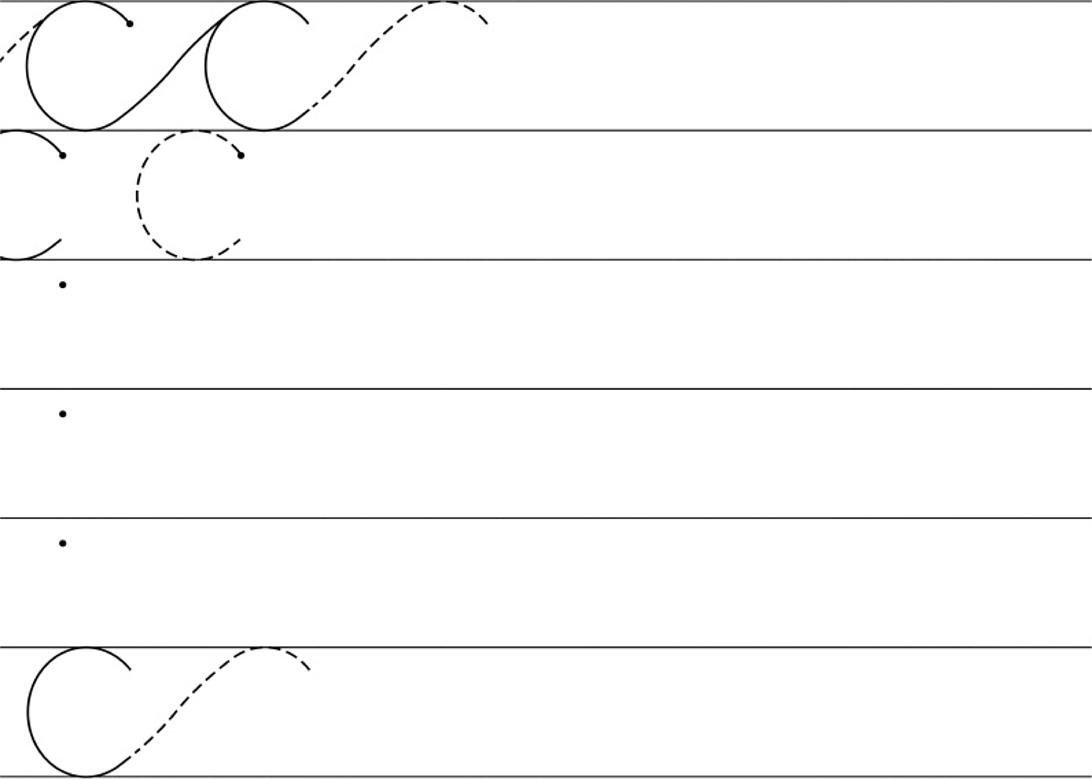

| LO 4.1.1 | LO 4.1.2 | LO 4.1.3 |

| LO 3.1 | LO 4.6.4 | LO 3.4.3 | LO 3.5.10 |
Learning Outcome 1: LISTENING: The learner is able to listen for information and enjoyment and respond appropriately and critically in a wider range of situations.
Assessment Standard 1.1: We know this when the learner listens attentively to questions, instructions and announcements and responds appropriately;
Assessment Standard 1.2: We know this when the learner demonstrates appropriate listening behaviour by listening without interrupting, showing respect for the speaker, and taking turns to speak, and asking questions for clarification;
Assessment Standard 1.3: We know this when the learner listens with enjoyment to short stories, rhymes, poems and songs from a variety of cultures, and shows understanding;
Learning Outcome 2: SPEAKING : The learner is able to communicate confidently and effectively in spoken language in a wide range of situations.
Assessment Standard 2.8: We know this when the learner contributes to class discussions;
2.8.3 responds to questions asked by listeners.
Learning Outcome 3: READING AND VIEWING : The learner is able to read and view for information and enjoyment and respond critically to the aesthetic, cultural and emotional values in texts.
Assessment Standard 3.1: We know this when the learner uses visual cues to make meaning;
Assessment Standard 3.4: We know this when the learner recognises letters and words and makes meaning of written text:
3.4.3 uses phonic and word recognition skills to decode new or unfamiliar words in context (e.g. visual cues like shape of word and letter patterns, picture clues context clues, and letter-sound relationships);
Assessment Standard 3.5: We know this when the learner develops phonic awareness:
3.5.10 recognises some high-frequency sight words such as ‘the’, ‘a’, ‘to’, ‘my’, your’, ‘like’ and including own name and print in the environment.
Learning Outcome 4: WRITING : The learner is able to write different kinds of factual and imaginative texts for a wide range of purposes.
Assessment Standard 4.1: We know this when the learner writes with increasing legibility:
4.1.1 manipulates writing tools like crayons and pencils effectively;
4.1.3 forms letters of the alphabet successfully;
Assessment Standard 4.6: We know this when the learner begins to build vocabulary and starts to spell words so that they can be read and understood by others:
4.6.4 builds own word bank and personal dictionary.
Learning Outcome 5: THINKING AND REASONING : The learner is able to use language to think and reason, and access, process and use information for learning.
Assessment Standard 5.1: We know this when the learner uses language to develop concepts:
5.1.2 understands and uses the conceptual language of different learning areas necessary at this level and in preparation for the next level.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English home language grade 1' conversation and receive update notifications?