| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In Grade 2 the learners will build new experiences in the additional language on those learnt in Grade 1 as well as those learnt in their Home Language. They will continue to need many listening and speaking opportunities so as to develop their reading and writing skills in Grade 2.
A wide vocabulary is very important. The ICS modules for Grade 2 provide opportunities for the revision of Grade 1 vocabulary and they gradually introduce and consolidate new vocabulary by means of poems, rhymes, stories, riddles and jokes and games to play.
Learners are encouraged to answer questions, and to take part in discussions and conversations on familiar topics.
The attention is drawn to the sounds of letters in the additional language and learners discover that some letters sound the same as in their home language whereas others differ.
Although the educator will attend to correct pronunciation at this stage, learners should always be encouraged to speak the additional language without feeling incompetent and self-conscious.
By keeping the dictionary pages at the end of each module in a file, learners can revise the vocabulary and use these lists as a personal dictionary to which they can refer when completing or writing sentences and stories.
Time scheduled for the modules 1 to 8
It is suggested that the average learners complete all eight modules during the year, completing ± two modules per term.
The slower learners will proceed at their own pace while the quick learners can be given more tasks if necessary.
All learners in Grade 2 should be exposed to all the listening, speaking and reading activities in these eight modules to ensure that progression occurs throughout.
Cas is one of many creatures living in the hedge around Farmer Brown’s farm. The characteristics of chameleons and the dangers which they must confront are described in the stories and poem to be listened to and read.
More nursery rhymes, riddles and phonic exercises are included.
Integration of themes
Cas’s environment also needs to be a safe one in order to survive. Discuss the dangers that the chameleon has to face and compare these to the dangers the learners have to be aware of in their immediate environment.
Discuss “the survival of the fittest”.
Cas did not move.
He stood very still.
He did not move his eyes.
He did not move his toes.
He did not move his long tail.
He saw the grey cat.
He did not like the grey cat.
He did not like the big black dog.
He did not like the owl on the fence.
The grey cat came nearer and nearer.
The grey cat stretched his front legs.
The grey cat stretched his hind legs.
He stretched his back.
He stretched his long, furry tail.
He sat in the sun under the hedge.
Still Cas could not move.
If he did, the grey cat would see him.
But Cas was hungry.
He was so very hungry.
“I wish this big, fat, grey cat would go away,” he thought.
“Then I can look for something to eat.”
But the big, fat, grey cat stretched himself
out in the sun under the hedge.
| LO 1.1 | LO 3.2.1 | LO 3.4.8 |
1. Where was Cas?
2. How did Cas feel? Why?
3. What do you think is going to happen?
4. What do you think of the grey cat?
5. What do you think Cas should do?
6. Do you know what kind of food Cas will be looking for?
7. Try and find a chameleon and describe his body, his toes, his eyes, his tongue and his tail.
8. Put the chameleon on different colours of paper – green, brown, yellow, black and watch what happens.
Cas lived in the ................................................................. house/hedge/burrow
Cas heard the ................................. in the long grass. Owls/dogs/lions
Cas was afraid of the .................................................... grey cat/river/forest
| LO 1.1.7 | LO 4.3 | LO 6.1 |
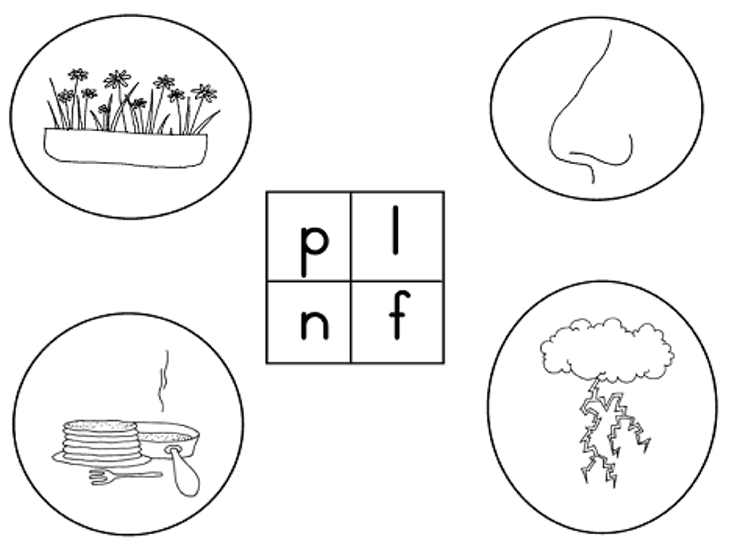
| LO 3.4.2 |
| Cas | the | walked | along | branch |
1. Cas ……………………………………………………………………………...
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
| big | The | cat | fat | grey |
| was | in | asleep | sun | the |
2. The ……………………………………………………………………………...
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
| did | Cas | move | not |
3. Cas……………………………………………………………………………...
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
| LO 4.5 | LO 4.6 |
Learning Outcome 1: LISTENING : The learner is able to listen for information and enjoyment and respond appropriately and critically in a wider range of situations.
Assessment Standard 1.1: We know this when the learner understands short, simple stories;
Learning Outcome 3: READING AND VIEWING : The learner is able to read and view for information and enjoyment, and respond critically to the aesthetic, cultural and emotional values in texts;
Assessment Standard 3.2: We know this when the learner begins to make meaning of written text by reading with the teacher:
3.2.1 reads the title and predicts what a book is about;
Assessment Standard 3.4: We know this when the learner develops phonic awareness:
3.4.2 understands the letter-sound relationships of most single consonants and short forms of vowels in words;
3.4.8 recognises on sight an increasing number of high-frequency words;
Learning Outcome 4: WRITING : The learner is able to write different kinds of factual and imaginative texts for a wide range of purposes;
Assessment Standard 4.5: We know this when the learner puts jumbled sentences in the right order and copies them;
Assessment Standard 4.6: We know this when the learner uses punctuation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English first additional language grade 2' conversation and receive update notifications?