| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
6. 12
7 (a) 18
(b) 13
(c) 17
(d) 19
(e) 12
Sum: 45
2.1
8.
| 1 | 14 | 7 | 12 |
| 15 | 4 | 9 | 6 |
| 10 | 5 | 16 | 3 |
| 8 | 11 | 2 | 13 |
Sum: 34
9. (a) 48
(b) 10
(c) 64
(d) 90
(e) 108
10. (a) true
(b) true
(c) false
(d) false
(e) true
11.
| _____ | _____ | _____ |
| _____ | _____ | _____ |
| _____ | _____ | _____ |
12.
| 9 969 | _____ | 9 699 | _____ |
| _____ | _____ | _____ | 6 669 |
| 6 966 | 9 669 | 6 696 | _____ |
| 6 699 | _____ | 6 969 | 9 666 |
13. Learners own assessment
6. Do you still remember?
The sum of all the numbers in a magic square is the same, whether they are arranged horizontally, vertically or diagonally.
What is the sum of the following magic square? _____________________________
| 1 | 8 | 3 |
| 6 | 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 0 | 7 |
7. Sometimes we substitute numbers with letters of the alphabet.
Look at the following magic square. Now replace the letters with the correct numbers.
| a | 11 | 16 | |
| b | 15 | c | |
| 14 | d | e |
What is the sum of the magic square? _____________________________
8. Brainteaser!
In the following magic square the numbers have been replaced by letters.
| c | 3k + 2c | k + 3c | 2k + 4c |
| 3k + 3c | 4c | 2k + c | k + 2c |
| 2k + 2c | k + c | 3k + 4c | 3c |
| k + 4c | 2k + 3c | 2c | 3k + c |
What is the sum of the magic square? ______________________________________
9. We can also assign values to particular letters, e.g.
a = 9 ; b = 6 ; c = 8 ; d = 2 ; e = 10 and f = 20
Calculate:
a) b x c = ________________________________
b) f ÷ d = ________________________________
c) a x b + e = ____________________________
d) (f – e) x a = ____________________________
e) [(c – d) + b] x a = _______________________
10. Replace the letters with any number of your choice and check whether the statements are true or false.
a) e + f = f + e _______________________
b) 2k + 2c = 2 x (k + c) _______________________
c) h – g = g – h _______________________
d) 4b = 4 + b _______________________
e) x + (y + z) = (x + y) + z _______________________
11. Brainteaser!
Construct you own magic square. Reduce the seven squares to five by moving only four of the toothpicks. Make a drawing of your attempt in the space that is provided and show which toothpicks have been moved to which position.
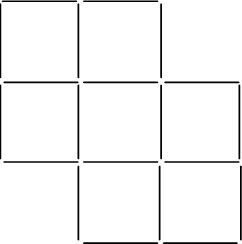
12. Another Brainteaser!
Can you complete the following magic square with numbers using 6's and/or 9's only? (Remember that the sum of the numbers in each row, column or diagonal must be
the same!)
| 6 666 | 6 996 | ||
| 9 696 | 6 999 | 9 966 | |
| 9 999 | |||
| 9 996 |
13. Time for self-assessment
Place a tick in the appropriate space.
| Unsure | Fairly sure | Very sure | |
| I am able to explain the following and to give an example: | ____ | ____ | ____ |
| a) square number | ____ | ____ | ____ |
| b) rectangular number | ____ | ____ | ____ |
| c) cubed number | ____ | ____ | ____ |
| I know a synonym for: | ____ | ____ | ____ |
| a) square number | ____ | ____ | ____ |
| b) cubed number | ____ | ____ | ____ |
| I can replace letters with numbers to complete a magic square | ____ | ____ | ____ |
| I can do the 4 main calculations correctly after having replaced the letters with numerical values | ____ | ____ | ____ |
Learning Outcome 1: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent numbers and their relationships, and to count, estimate, calculate and check with competence and confidence in solving problems.
Assessment Standard 1.7: We know this when the learner estimates and calculates by selecting and using operations appropriate to solving problems that involve:
1.7.2: multiple operations with integers;
Assessment Standard 1.9: We know this when the learner uses a range of techniques to perform calculations including:
1.9.1: using the commutative, associative and distributive properties with positive rational numbers and zero;
Assessment Standard 1.10: We know this when the learner uses a range of strategies to check solutions and judges the reasonableness of solutions.
Learning Outcome 2: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent patterns and relationships, as well as to solve problems using algebraic language and skills.
Assessment Standard 2.5: We know this when the learner solves or completes number sentences by inspection or by trial-and-improvement, checking the solutions by substitution (e.g. 2 x - 8 = 4).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?