| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
How much detail can ultrasound reveal? The image in [link] is typical of low-cost systems, but that in [link] shows the remarkable detail possible with more advanced systems, including 3D imaging. Ultrasound today is commonly used in prenatal care. Such imaging can be used to see if the fetus is developing at a normal rate, and help in the determination of serious problems early in the pregnancy. Ultrasound is also in wide use to image the chambers of the heart and the flow of blood within the beating heart, using the Doppler effect (echocardiology).
Whenever a wave is used as a probe, it is very difficult to detect details smaller than its wavelength . Indeed, current technology cannot do quite this well. Abdominal scans may use a 7-MHz frequency, and the speed of sound in tissue is about 1540 m/s—so the wavelength limit to detail would be . In practice, 1-mm detail is attainable, which is sufficient for many purposes. Higher-frequency ultrasound would allow greater detail, but it does not penetrate as well as lower frequencies do. The accepted rule of thumb is that you can effectively scan to a depth of about into tissue. For 7 MHz, this penetration limit is , which is 0.11 m. Higher frequencies may be employed in smaller organs, such as the eye, but are not practical for looking deep into the body.
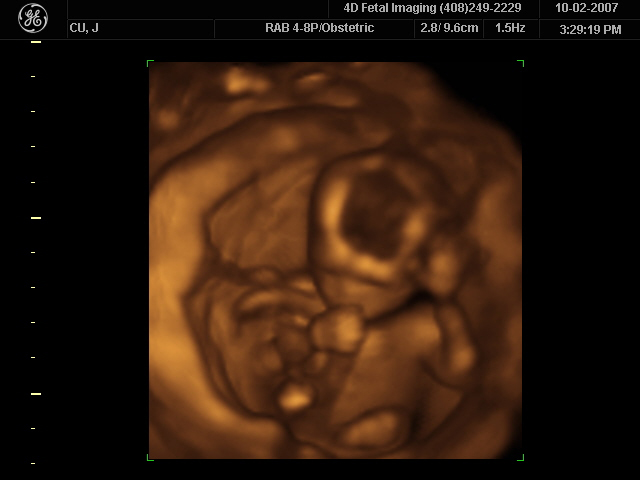
In addition to shape information, ultrasonic scans can produce density information superior to that found in X-rays, because the intensity of a reflected sound is related to changes in density. Sound is most strongly reflected at places where density changes are greatest.
Another major use of ultrasound in medical diagnostics is to detect motion and determine velocity through the Doppler shift of an echo, known as Doppler-shifted ultrasound . This technique is used to monitor fetal heartbeat, measure blood velocity, and detect occlusions in blood vessels, for example. (See [link] .) The magnitude of the Doppler shift in an echo is directly proportional to the velocity of whatever reflects the sound. Because an echo is involved, there is actually a double shift. The first occurs because the reflector (say a fetal heart) is a moving observer and receives a Doppler-shifted frequency. The reflector then acts as a moving source, producing a second Doppler shift.
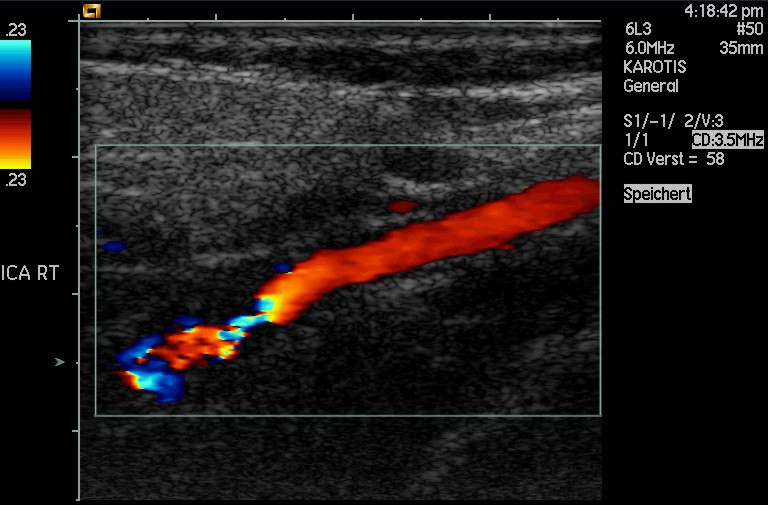
A clever technique is used to measure the Doppler shift in an echo. The frequency of the echoed sound is superimposed on the broadcast frequency, producing beats. The beat frequency is , and so it is directly proportional to the Doppler shift ( ) and hence, the reflector’s velocity. The advantage in this technique is that the Doppler shift is small (because the reflector’s velocity is small), so that great accuracy would be needed to measure the shift directly. But measuring the beat frequency is easy, and it is not affected if the broadcast frequency varies somewhat. Furthermore, the beat frequency is in the audible range and can be amplified for audio feedback to the medical observer.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics ii' conversation and receive update notifications?