| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
where λ is the center wavelength, n is the refractive index of the medium, ∆λ is the spectral width of the source. In this way good contrast fringes can be obtained only when the lengths of interfering beams pathways are closed to each other. If we will vary the length of a pathway of a beam reflected from sample, the height of a sample can be determined by looking at the position for which a fringe contrast is a maximum. In this case interference pattern exist only over a very shallow depth of the surface. When we vary a pathway of sample-reflected beam we also move the sample in a vertical direction in order to get the phase at which maximum intensity of fringes will be achieved. This phase will be converted in height of a point at the sample surface.
The combination of phase shift technology with white-light source provides a very powerful tool to measure the topography of quite rough surfaces with the amplitude in heights about and the precision up to 1-2 nm. Through a developed software package for quantitatively evaluating the resulting interferogram, the proposed system can retrieve the surface profile and topography of the sample objects [link] .
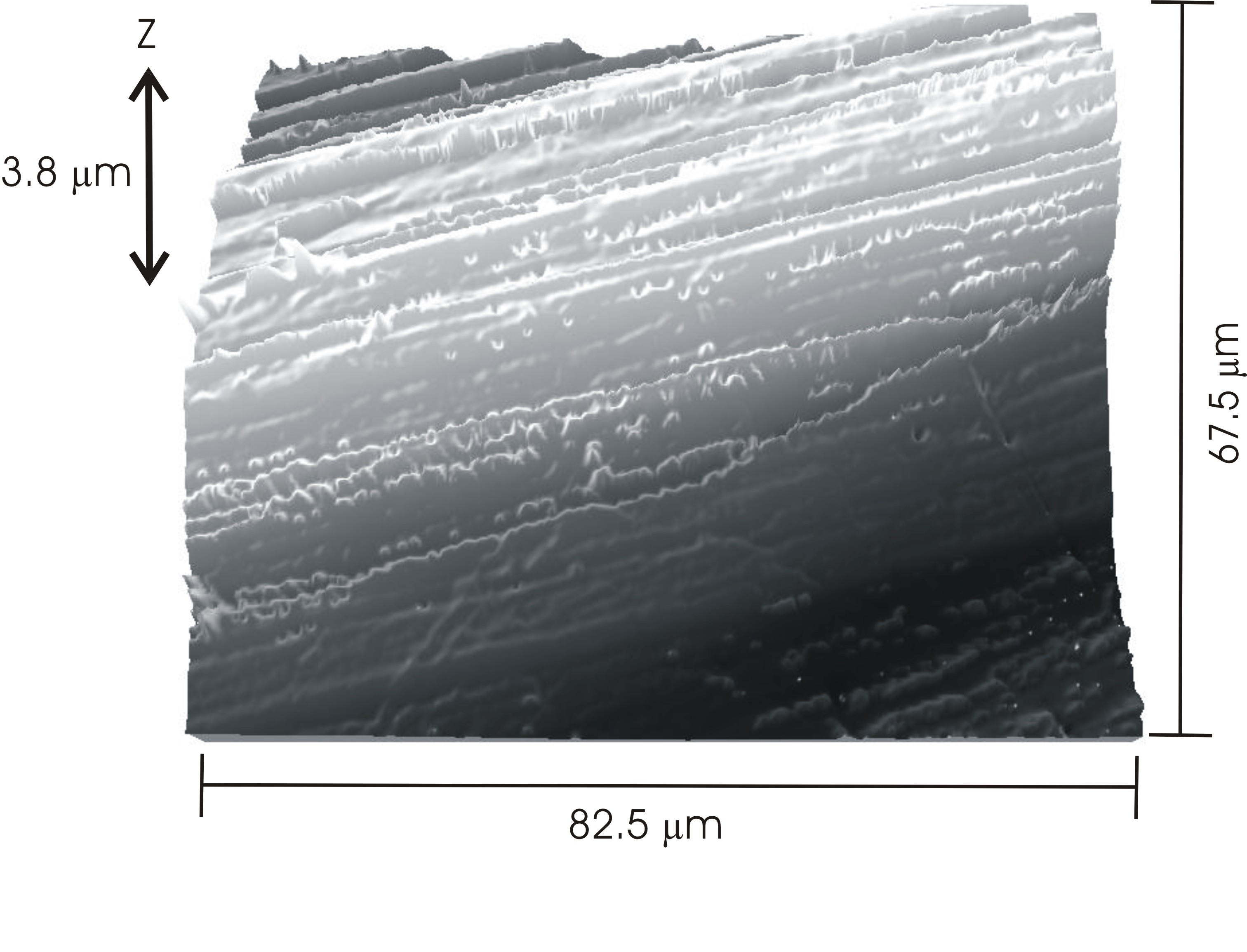
Except the interferometric methods described above, there are a several other microscopic techniques for studying crystal surface topography. The most common are scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). All these techniques are used to obtain information about the surface structure. However they differ from each other by the physical principles on which they based.
SEM allows us to obtain images of surface topography with the resolution much higher than the conventional light microscopes do. Also it is able to provide information about other surface characteristics such as chemical composition, electrical conductivity etc, see [link] . All types of data are generated by the reflecting of accelerated electron beams from the sample surface. When electrons strike the sample surface, they lose their energy by repeated random scattering and adsorption within an outer layer into the depth varying from 100 nm to 5 microns.
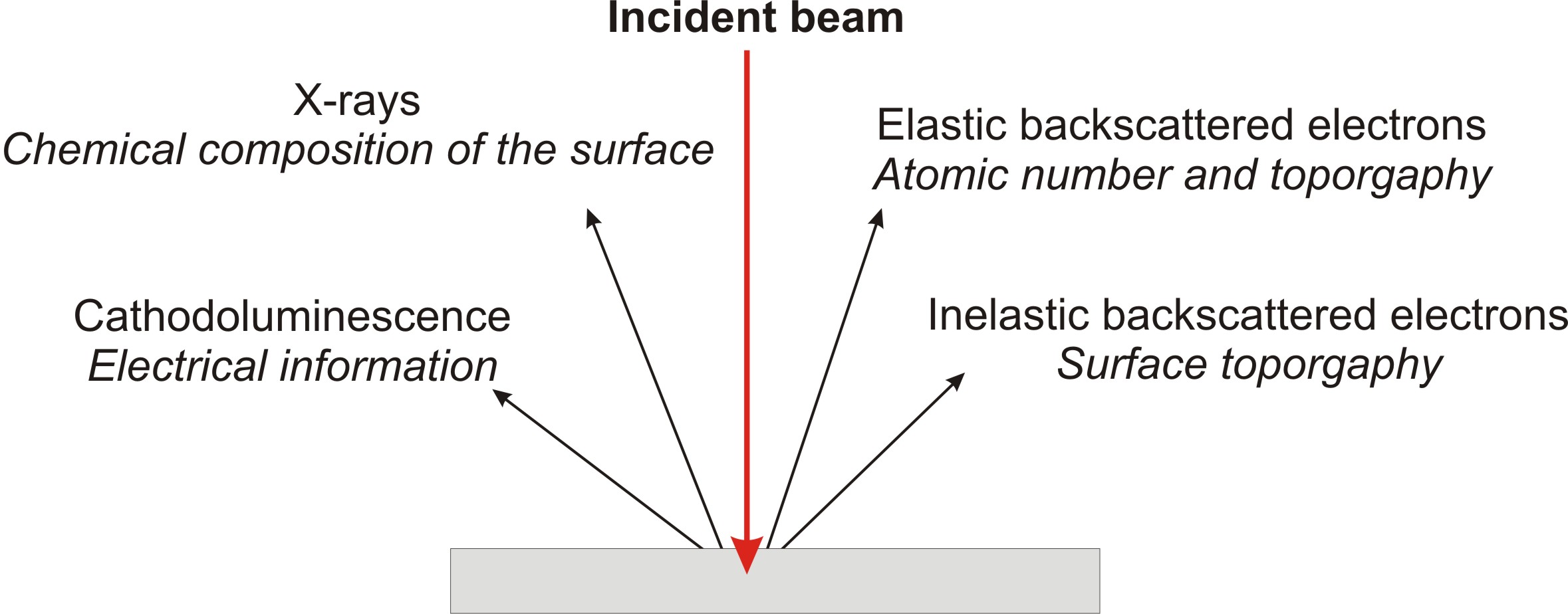
The thickness of this outer layer also knows as interactive layer depends on energy of electrons in the beam, composition and density of a sample. Result of the interaction between electron beam and the surface provides several types of signals. The main type is secondary or inelastic scattered electrons. They are produced as a result of interaction between the beam of electrons and weakly bound electrons in the conduction band of the sample. Secondary electrons are ejected from the k-orbitals of atoms within the surface layer of thickness about a few nanometers. This is because secondary electrons are low energy electrons (<50 eV), so only those formed within the first few nanometers of the sample surface have enough energy to escape and be detected. Secondary backscattered electrons provide the most common signal to investigate surface topography with lateral resolution up to 0.4 - 0.7 nm.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Nanomaterials and nanotechnology' conversation and receive update notifications?