| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The wavelength of green light ranges between 500 nm an d 565 nm. Calculate the range of frequencies that correspond to this range of wavelengths.
Use
to determine .
The range of frequencies of green light is to .
White light, like the light which comes from the sun, is made up of all the visible wavelengths of light. In other words, white light is a combination of all the colours of visible light.
You learnt that the speed of light is different in different substances. The speed of light in different substances depends on the frequency of the light. For example, when white light travels through glass, light of the different frequencies is slowed down by different amounts. The lower the frequency, the less the speed is reduced which means that red light (lowest frequency) is slowed down less than violet light (highest frequency). We can see this when white light is incident on a glass prism.
Have a look at the picture below. When the white light hits the edge of the prism, the light which travels through the glass is refracted as it moves from the less dense medium (air) to the more dense medium (glass).
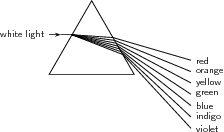
When the light hits the other side of the prism it is again refracted but the angle of the prism edge allows the light to remain separated into its different colours. White light is therefore separated into its different colours by the prism and we say that the white light has been dispersed by the prism.
The dispersion effect is also responsible for why we see rainbows. When sunlight hits drops of water in the atmosphere, the white light is dispersed into its different colours by the water.
The primary colours of light are red , green and blue . When all the primary colours are superposed (added together), white light is produced. Red, green and blue are therefore called the additive primary colours . All the other colours can be produced by different combinations of red, green and blue.
The subtractive primary colours are obtained by subtracting one of the three additive primary colours from white light. The subtractive primary colours are yellow , magenta and cyan . Magenta appears as a pinkish-purplish colour and cyan looks greenish-blue. You can see how the primary colours of light add up to the different subtractive colours in the illustration below.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?