| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Historically, heroin has been a major opioid drug of abuse ( [link] ). Heroin can be snorted, smoked, or injected intravenously. Like the stimulants described earlier, the use of heroin is associated with an initial feeling of euphoria followed by periods of agitation. Because heroin is often administered via intravenous injection, users often bear needle track marks on their arms and, like all abusers of intravenous drugs, have an increased risk for contraction of both tuberculosis and HIV.
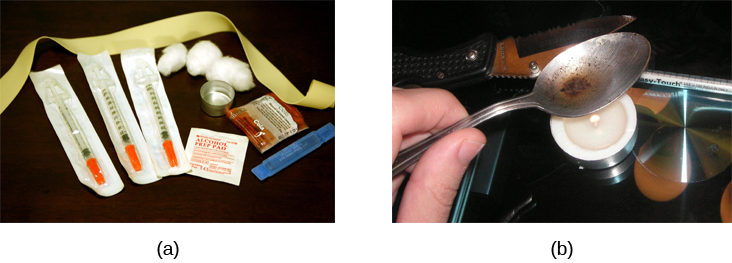
Aside from their utility as analgesic drugs, opioid-like compounds are often found in cough suppressants, anti-nausea, and anti-diarrhea medications. Given that withdrawal from a drug often involves an experience opposite to the effect of the drug, it should be no surprise that opioid withdrawal resembles a severe case of the flu. While opioid withdrawal can be extremely unpleasant, it is not life-threatening (Julien, 2005). Still, people experiencing opioid withdrawal may be given methadone to make withdrawal from the drug less difficult. Methadone is a synthetic opioid that is less euphorigenic than heroin and similar drugs. Methadone clinics help people who previously struggled with opioid addiction manage withdrawal symptoms through the use of methadone. Other drugs, including the opioid buprenorphine, have also been used to alleviate symptoms of opiate withdrawal.
Codeine is an opioid with relatively low potency. It is often prescribed for minor pain, and it is available over-the-counter in some other countries. Like all opioids, codeine does have abuse potential. In fact, abuse of prescription opioid medications is becoming a major concern worldwide (Aquina, Marques-Baptista, Bridgeman,&Merlin, 2009; Casati, Sedefov,&Pfeiffer-Gerschel, 2012).
A hallucinogen is one of a class of drugs that results in profound alterations in sensory and perceptual experiences ( [link] ). In some cases, users experience vivid visual hallucinations. It is also common for these types of drugs to cause hallucinations of body sensations (e.g., feeling as if you are a giant) and a skewed perception of the passage of time.

As a group, hallucinogens are incredibly varied in terms of the neurotransmitter systems they affect. Mescaline and LSD are serotonin agonists, and PCP (angel dust) and ketamine (an animal anesthetic) act as antagonists of the NMDA glutamate receptor. In general, these drugs are not thought to possess the same sort of abuse potential as other classes of drugs discussed in this section.
To learn more about some of the most commonly abused prescription and street drugs, check out the Commonly Abused Drugs Chart and the Commonly Abused Prescription Drugs Chart from the National Institute on Drug Abuse.
While the possession and use of marijuana is illegal in most states, it is now legal in Washington and Colorado to possess limited quantities of marijuana for recreational use ( [link] ). In contrast, medical marijuana use is now legal in nearly half of the United States and in the District of Columbia. Medical marijuana is marijuana that is prescribed by a doctor for the treatment of a health condition. For example, people who undergo chemotherapy will often be prescribed marijuana to stimulate their appetites and prevent excessive weight loss resulting from the side effects of chemotherapy treatment. Marijuana may also have some promise in the treatment of a variety of medical conditions (Mather, Rauwendaal, Moxham-Hall,&Wodak, 2013; Robson, 2014; Schicho&Storr, 2014).

While medical marijuana laws have been passed on a state-by-state basis, federal laws still classify this as an illicit substance, making conducting research on the potentially beneficial medicinal uses of marijuana problematic. There is quite a bit of controversy within the scientific community as to the extent to which marijuana might have medicinal benefits due to a lack of large-scale, controlled research (Bostwick, 2012). As a result, many scientists have urged the federal government to allow for relaxation of current marijuana laws and classifications in order to facilitate a more widespread study of the drug’s effects (Aggarwal et al., 2009; Bostwick, 2012; Kogan&Mechoulam, 2007).
Until recently, the United States Department of Justice routinely arrested people involved and seized marijuana used in medicinal settings. In the latter part of 2013, however, the United States Department of Justice issued statements indicating that they would not continue to challenge state medical marijuana laws. This shift in policy may be in response to the scientific community’s recommendations and/or reflect changing public opinion regarding marijuana.
Substance use disorder is defined in DSM-5 as a compulsive pattern of drug use despite negative consequences. Both physical and psychological dependence are important parts of this disorder. Alcohol, barbiturates, and benzodiazepines are central nervous system depressants that affect GABA neurotransmission. Cocaine, amphetamine, cathinones, and MDMA are all central nervous stimulants that agonize dopamine neurotransmission, while nicotine and caffeine affect acetylcholine and adenosine, respectively. Opiate drugs serve as powerful analgesics through their effects on the endogenous opioid neurotransmitter system, and hallucinogenic drugs cause pronounced changes in sensory and perceptual experiences. The hallucinogens are variable with regards to the specific neurotransmitter systems they affect.
Many people experiment with some sort of psychoactive substance at some point in their lives. Why do you think people are motivated to use substances that alter consciousness?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?