| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A transverse wave is traveling left to right. Which of the following is correct about the motion of particles in the wave?
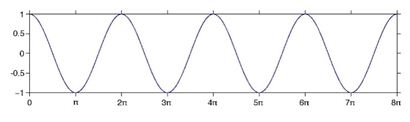
The graph shows propagation of a mechanical wave. What is the wavelength of this wave?
Give one example of a transverse wave and another of a longitudinal wave, being careful to note the relative directions of the disturbance and wave propagation in each.
What is the difference between propagation speed and the frequency of a wave? Does one or both affect wavelength? If so, how?
Storms in the South Pacific can create waves that travel all the way to the California coast, which are 12,000 km away. How long does it take them if they travel at 15.0 m/s?
Waves on a swimming pool propagate at 0.750 m/s. You splash the water at one end of the pool and observe the wave go to the opposite end, reflect, and return in 30.0 s. How far away is the other end of the pool?
Wind gusts create ripples on the ocean that have a wavelength of 5.00 cm and propagate at 2.00 m/s. What is their frequency?
How many times a minute does a boat bob up and down on ocean waves that have a wavelength of 40.0 m and a propagation speed of 5.00 m/s?
Scouts at a camp shake the rope bridge they have just crossed and observe the wave crests to be 8.00 m apart. If they shake it the bridge twice per second, what is the propagation speed of the waves?
What is the wavelength of the waves you create in a swimming pool if you splash your hand at a rate of 2.00 Hz and the waves propagate at 0.800 m/s?
What is the wavelength of an earthquake that shakes you with a frequency of 10.0 Hz and gets to another city 84.0 km away in 12.0 s?
Radio waves transmitted through space at by the Voyager spacecraft have a wavelength of 0.120 m. What is their frequency?
Your ear is capable of differentiating sounds that arrive at the ear just 1.00 ms apart. What is the minimum distance between two speakers that produce sounds that arrive at noticeably different times on a day when the speed of sound is 340 m/s?
(a) Seismographs measure the arrival times of earthquakes with a precision of 0.100 s. To get the distance to the epicenter of the quake, they compare the arrival times of S- and P-waves, which travel at different speeds. [link] ) If S- and P-waves travel at 4.00 and 7.20 km/s, respectively, in the region considered, how precisely can the distance to the source of the earthquake be determined? (b) Seismic waves from underground detonations of nuclear bombs can be used to locate the test site and detect violations of test bans. Discuss whether your answer to (a) implies a serious limit to such detection. (Note also that the uncertainty is greater if there is an uncertainty in the propagation speeds of the S- and P-waves.)


Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?