| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

An electric dipole (with +2 q and –2 q as the two charges) is shown in the figure above. A third charge, − q is placed equidistant from the dipole charges. What will be the direction of the net force on the third charge?
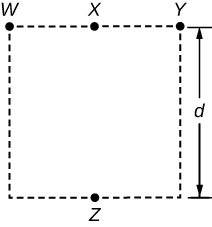
Four objects, each with charge + q , are held fixed on a square with sides of length d , as shown in the figure. Objects X and Z are at the midpoints of the sides of the square. The electrostatic force exerted by object W on object X is F . Use this information to answer questions 39–40.
What is the magnitude of force exerted by object W on Z ?
(b)
What is the magnitude of the net force exerted on object X by objects W , Y , and Z ?
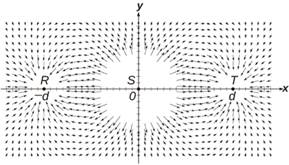
The figure above represents the electric field in the vicinity of three small charged objects, R , S , and T . The objects have charges − q , +2 q , and − q , respectively, and are located on the x -axis at − d , 0, and d . Field vectors of very large magnitude are omitted for clarity.
(a) i) Briefly describe the characteristics of the field diagram that indicate that the sign of the charges of objects R and T is negative and that the sign of the charge of object S is positive.
ii) Briefly describe the characteristics of the field diagram that indicate that the magnitudes of the charges of objects R and T are equal and that the magnitude of the charge of object S is about twice that of objects R and T .
For the following parts, an electric field directed to the right is defined to be positive.
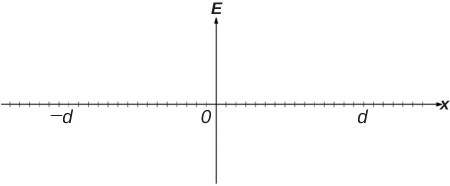
(b) On the axes below, sketch a graph of the electric field E along the x -axis as a function of position x .
(c) Write an expression for the electric field E along the x -axis as a function of position x in the region between objects S and T in terms of q , d , and fundamental constants, as appropriate.
(d) Your classmate tells you there is a point between S and T where the electric field is zero. Determine whether this statement is true, and explain your reasoning using two of the representations from parts (a), (b), or (c).
(a) i) Field vectors near objects point toward negatively charged objects and away from positively charged objects.
(a) ii) The vectors closest to R and T are about the same length and start at about the same distance. We have that , so the charge on R is about the same as the charge on T . The closest vectors around S are about the same length as those around R and T . The vectors near S start at about 6 units away, while vectors near R and T start at about 4 units. We have that , so , and so the charge on S is about twice that on R and T .
(b)
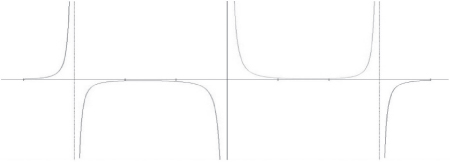
(c)
(d) The statement is not true. The vector diagram shows field vectors in this region with nonzero length, and the vectors not shown have even greater lengths. The equation in part (c) shows that, when , the denominator of the negative term is always greater than the denominator of the third term, but the numerator is the same. So the negative term always has a smaller magnitude than the third term and since the second term is positive the sum of the terms is always positive.
Compare and contrast the Coulomb force field and the electric field. To do this, make a list of five properties for the Coulomb force field analogous to the five properties listed for electric field lines. Compare each item in your list of Coulomb force field properties with those of the electric field—are they the same or different? (For example, electric field lines cannot cross. Is the same true for Coulomb field lines?)
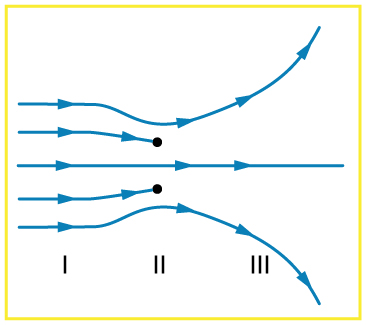
[link] shows an electric field extending over three regions, labeled I, II, and III. Answer the following questions. (a) Are there any isolated charges? If so, in what region and what are their signs? (b) Where is the field strongest? (c) Where is it weakest? (d) Where is the field the most uniform?
(a) Sketch the electric field lines near a point charge . (b) Do the same for a point charge .
Sketch the electric field lines a long distance from the charge distributions shown in [link] (a) and (b)
[link] shows the electric field lines near two charges and . What is the ratio of their magnitudes? (b) Sketch the electric field lines a long distance from the charges shown in the figure.
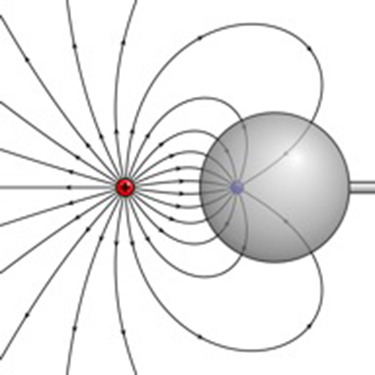
Sketch the electric field lines in the vicinity of two opposite charges, where the negative charge is three times greater in magnitude than the positive. (See [link] for a similar situation).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?