| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
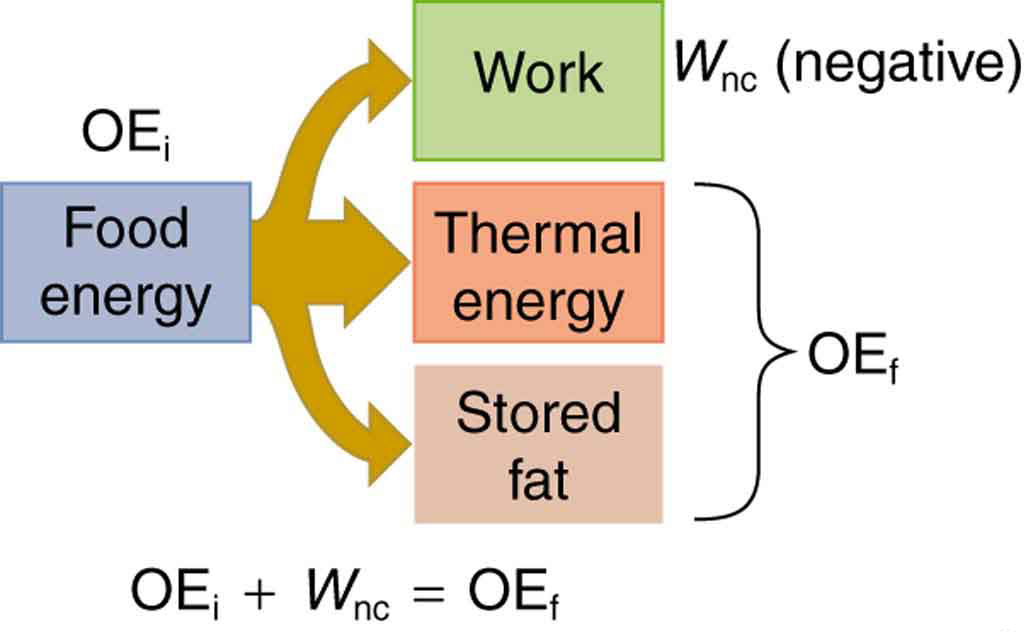
Our own bodies, like all living organisms, are energy conversion machines. Conservation of energy implies that the chemical energy stored in food is converted into work, thermal energy, and/or stored as chemical energy in fatty tissue. (See [link] .) The fraction going into each form depends both on how much we eat and on our level of physical activity. If we eat more than is needed to do work and stay warm, the remainder goes into body fat.
The rate at which the body uses food energy to sustain life and to do different activities is called the metabolic rate . The total energy conversion rate of a person at rest is called the basal metabolic rate (BMR) and is divided among various systems in the body, as shown in [link] . The largest fraction goes to the liver and spleen, with the brain coming next. Of course, during vigorous exercise, the energy consumption of the skeletal muscles and heart increase markedly. About 75% of the calories burned in a day go into these basic functions. The BMR is a function of age, gender, total body weight, and amount of muscle mass (which burns more calories than body fat). Athletes have a greater BMR due to this last factor.
| Organ | Power consumed at rest (W) | Oxygen consumption (mL/min) | Percent of BMR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liver&spleen | 23 | 67 | 27 |
| Brain | 16 | 47 | 19 |
| Skeletal muscle | 15 | 45 | 18 |
| Kidney | 9 | 26 | 10 |
| Heart | 6 | 17 | 7 |
| Other | 16 | 48 | 19 |
| Totals | 85 W | 250 mL/min | 100% |
Energy consumption is directly proportional to oxygen consumption because the digestive process is basically one of oxidizing food. We can measure the energy people use during various activities by measuring their oxygen use. (See [link] .) Approximately 20 kJ of energy are produced for each liter of oxygen consumed, independent of the type of food. [link] shows energy and oxygen consumption rates (power expended) for a variety of activities.
Work done by a person is sometimes called useful work , which is work done on the outside world , such as lifting weights. Useful work requires a force exerted through a distance on the outside world, and so it excludes internal work, such as that done by the heart when pumping blood. Useful work does include that done in climbing stairs or accelerating to a full run, because these are accomplished by exerting forces on the outside world. Forces exerted by the body are nonconservative, so that they can change the mechanical energy ( ) of the system worked upon, and this is often the goal. A baseball player throwing a ball, for example, increases both the ball’s kinetic and potential energy.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?