| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Faraday’s experiments showed that the emf induced by a change in magnetic flux depends on only a few factors. First, emf is directly proportional to the change in flux . Second, emf is greatest when the change in time is smallest—that is, emf is inversely proportional to . Finally, if a coil has turns, an emf will be produced that is times greater than for a single coil, so that emf is directly proportional to . The equation for the emf induced by a change in magnetic flux is
This relationship is known as Faraday’s law of induction . The units for emf are volts, as is usual.
The minus sign in Faraday’s law of induction is very important. The minus means that the emf creates a current I and magnetic field B that oppose the change in flux —this is known as Lenz’s law . The direction (given by the minus sign) of the emf is so important that it is called Lenz’s law after the Russian Heinrich Lenz (1804–1865), who, like Faraday and Henry, independently investigated aspects of induction. Faraday was aware of the direction, but Lenz stated it so clearly that he is credited for its discovery. (See [link] .)
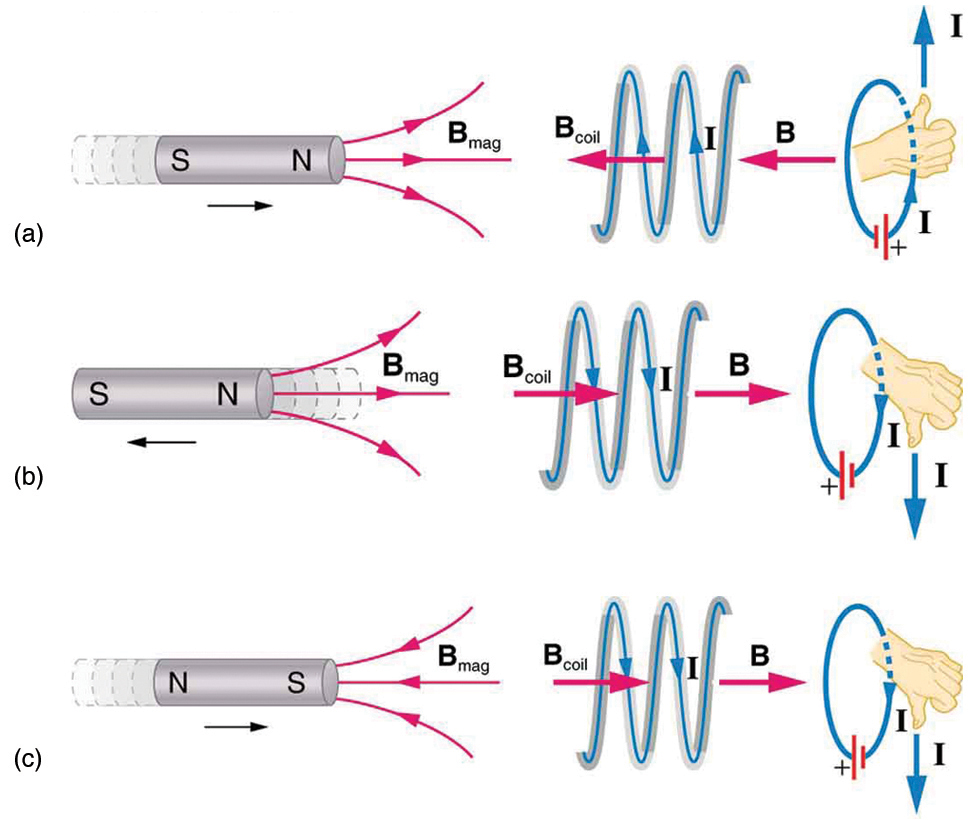
To use Lenz’s law to determine the directions of the induced magnetic fields, currents, and emfs:
For practice, apply these steps to the situations shown in [link] and to others that are part of the following text material.
There are many applications of Faraday’s Law of induction, as we will explore in this chapter and others. At this juncture, let us mention several that have to do with data storage and magnetic fields. A very important application has to do with audio and video recording tapes . A plastic tape, coated with iron oxide, moves past a recording head. This recording head is basically a round iron ring about which is wrapped a coil of wire—an electromagnet ( [link] ). A signal in the form of a varying input current from a microphone or camera goes to the recording head. These signals (which are a function of the signal amplitude and frequency) produce varying magnetic fields at the recording head. As the tape moves past the recording head, the magnetic field orientations of the iron oxide molecules on the tape are changed thus recording the signal. In the playback mode, the magnetized tape is run past another head, similar in structure to the recording head. The different magnetic field orientations of the iron oxide molecules on the tape induces an emf in the coil of wire in the playback head. This signal then is sent to a loudspeaker or video player.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?