| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
During the antebellum years, wealthy southern planters formed an elite master class that wielded most of the economic and political power of the region. They created their own standards of gentility and honor, defining ideals of southern white manhood and womanhood and shaping the culture of the South. To defend the system of forced labor on which their economic survival and genteel lifestyles depended, elite southerners developed several proslavery arguments that they levied at those who would see the institution dismantled.
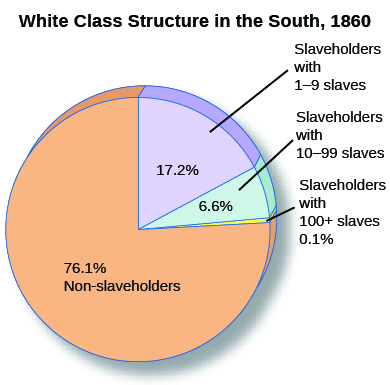
The South prospered, but its wealth was very unequally distributed. Upward social mobility did not exist for the millions of slaves who produced a good portion of the nation’s wealth, while poor southern whites envisioned a day when they might rise enough in the world to own slaves of their own. Because of the cotton boom, there were more millionaires per capita in the Mississippi River Valley by 1860 than anywhere else in the United States. However, in that same year, only 3 percent of whites owned more than fifty slaves, and two-thirds of white households in the South did not own any slaves at all ( [link] ). Distribution of wealth in the South became less democratic over time; fewer whites owned slaves in 1860 than in 1840.
At the top of southern white society stood the planter elite, which comprised two groups. In the Upper South, an aristocratic gentry, generation upon generation of whom had grown up with slavery, held a privileged place. In the Deep South, an elite group of slaveholders gained new wealth from cotton. Some members of this group hailed from established families in the eastern states (Virginia and the Carolinas), while others came from humbler backgrounds. South Carolinian Nathaniel Heyward, a wealthy rice planter and member of the aristocratic gentry, came from an established family and sat atop the pyramid of southern slaveholders. He amassed an enormous estate; in 1850, he owned more than eighteen hundred slaves. When he died in 1851, he left an estate worth more than $2 million (approximately $63 million in 2014 dollars).
As cotton production increased, new wealth flowed to the cotton planters. These planters became the staunchest defenders of slavery, and as their wealth grew, they gained considerable political power.
One member of the planter elite was Edward Lloyd V, who came from an established and wealthy family of Talbot County, Maryland. Lloyd had inherited his position rather than rising to it through his own labors. His hundreds of slaves formed a crucial part of his wealth. Like many of the planter elite, Lloyd’s plantation was a masterpiece of elegant architecture and gardens ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'U.s. history' conversation and receive update notifications?