Some weak acids and weak bases ionize to such an extent that the simplifying assumption that
x is small relative to the initial concentration of the acid or base is inappropriate. As we solve for the equilibrium concentrations in such cases, we will see that we cannot neglect the change in the initial concentration of the acid or base, and we must solve the equilibrium equations by using the quadratic equation.
Equilibrium concentrations in a solution of a weak acid
Sodium bisulfate, NaHSO
4 , is used in some household cleansers because it contains the
ion, a weak acid. What is the pH of a 0.50-
M solution of
Solution
We need to determine the equilibrium concentration of the hydronium ion that results from the ionization of
so that we can use
to determine the pH. As in the previous examples, we can approach the solution by the following steps:

-
Determine x and equilibrium concentrations . This table shows the changes and concentrations:
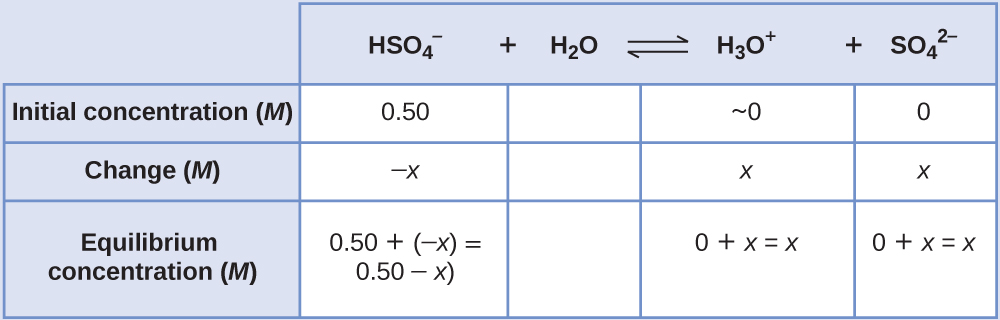
-
Solve for x and the concentrations . As we begin solving for
x , we will find this is more complicated than in previous examples. As we discuss these complications we should not lose track of the fact that it is still the purpose of this step to determine the value of
x .
At equilibrium:
If we assume that
x is small and approximate (0.50 −
x ) as 0.50, we find:
When we check the assumption, we calculate:
The value of
x is not less than 5% of 0.50, so the assumption is not valid. We need the quadratic formula to find
x .
The equation:
gives
or
This equation can be solved using the quadratic formula. For an equation of the form
x is given by the equation:
In this problem,
a = 1,
b = 1.2
10
−3 , and
c = −6.0
10
−3 .
Solving for
x gives a negative root (which cannot be correct since concentration cannot be negative) and a positive root:
Now determine the hydronium ion concentration and the pH:
The pH of this solution is:
Check your learning
(a) Show that the quadratic formula gives
x = 7.2
10
−2 .
(b) Calculate the pH in a 0.010-
M solution of caffeine, a weak base:
(Hint: It will be necessary to convert [OH
− ] to
or pOH to pH toward the end of the calculation.)
The relative strengths of strong acids and bases
Strong acids, such as HCl, HBr, and HI, all exhibit the same strength in water. The water molecule is such a strong base compared to the conjugate bases Cl
− , Br
− , and I
− that ionization of these strong acids is essentially complete in aqueous solutions. In solvents less basic than water, we find HCl, HBr, and HI differ markedly in their tendency to give up a proton to the solvent. For example, when dissolved in ethanol (a weaker base than water), the extent of ionization increases in the order HCl<HBr<HI, and so HI is demonstrated to be the strongest of these acids. The inability to discern differences in strength among strong acids dissolved in water is known as the
leveling effect of water .


