| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The action of water on P 4 O 6 , PCl 3 , PBr 3 , or PI 3 forms phosphorous acid, H 3 PO 3 (shown in [link] ). The best method for preparing pure phosphorous acid is by hydrolyzing phosphorus trichloride:
Heating the resulting solution expels the hydrogen chloride and leads to the evaporation of water. When sufficient water evaporates, white crystals of phosphorous acid will appear upon cooling. The crystals are deliquescent, very soluble in water, and have an odor like that of garlic. The solid melts at 70.1 °C and decomposes at about 200 °C by disproportionation into phosphine and orthophosphoric acid:
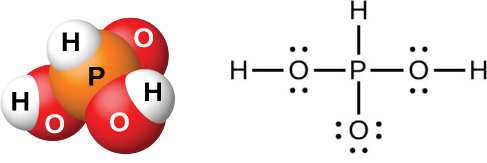
Phosphorous acid forms only two series of salts, which contain the dihydrogen phosphite ion, or the hydrogen phosphate ion, respectively. It is not possible to replace the third atom of hydrogen because it is not very acidic, as it is not easy to ionize the P-H bond.
The preparation of sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4 (shown in [link] ), begins with the oxidation of sulfur to sulfur trioxide and then converting the trioxide to sulfuric acid. Pure sulfuric acid is a colorless, oily liquid that freezes at 10.5 °C. It fumes when heated because the acid decomposes to water and sulfur trioxide. The heating process causes the loss of more sulfur trioxide than water, until reaching a concentration of 98.33% acid. Acid of this concentration boils at 338 °C without further change in concentration (a constant boiling solution) and is commercially concentrated H 2 SO 4 . The amount of sulfuric acid used in industry exceeds that of any other manufactured compound.
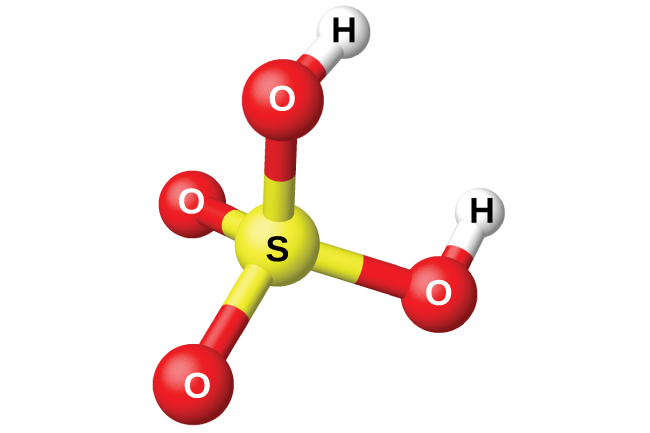
The strong affinity of concentrated sulfuric acid for water makes it a good dehydrating agent. It is possible to dry gases and immiscible liquids that do not react with the acid by passing them through the acid.
Sulfuric acid is a strong diprotic acid that ionizes in two stages. In aqueous solution, the first stage is essentially complete. The secondary ionization is not nearly so complete, and is a moderately strong acid (about 25% ionized in solution of a salt: K a = 1.2 10 −2 ).
Being a diprotic acid, sulfuric acid forms both sulfates, such as Na 2 SO 4 , and hydrogen sulfates, such as NaHSO 4 . Most sulfates are soluble in water; however, the sulfates of barium, strontium, calcium, and lead are only slightly soluble in water.
Among the important sulfates are Na 2 SO 4 ⋅10H 2 O and Epsom salts, MgSO 4 ⋅7H 2 O. Because the ion is an acid, hydrogen sulfates, such as NaHSO 4 , exhibit acidic behavior, and this compound is the primary ingredient in some household cleansers.
Hot, concentrated sulfuric acid is an oxidizing agent. Depending on its concentration, the temperature, and the strength of the reducing agent, sulfuric acid oxidizes many compounds and, in the process, undergoes reduction to SO 2 , S, H 2 S , or S 2− .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?