| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Although weight is related to mass, it is not the same thing. Weight refers to the force that gravity exerts on an object. This force is directly proportional to the mass of the object. The weight of an object changes as the force of gravity changes, but its mass does not. An astronaut’s mass does not change just because she goes to the moon. But her weight on the moon is only one-sixth her earth-bound weight because the moon’s gravity is only one-sixth that of the earth’s. She may feel “weightless” during her trip when she experiences negligible external forces (gravitational or any other), although she is, of course, never “massless.”
The law of conservation of matter summarizes many scientific observations about matter: It states that there is no detectable change in the total quantity of matter present when matter converts from one type to another (a chemical change) or changes among solid, liquid, or gaseous states (a physical change) . Brewing beer and the operation of batteries provide examples of the conservation of matter ( [link] ). During the brewing of beer, the ingredients (water, yeast, grains, malt, hops, and sugar) are converted into beer (water, alcohol, carbonation, and flavoring substances) with no actual loss of substance. This is most clearly seen during the bottling process, when glucose turns into ethanol and carbon dioxide, and the total mass of the substances does not change. This can also be seen in a lead-acid car battery: The original substances (lead, lead oxide, and sulfuric acid), which are capable of producing electricity, are changed into other substances (lead sulfate and water) that do not produce electricity, with no change in the actual amount of matter.
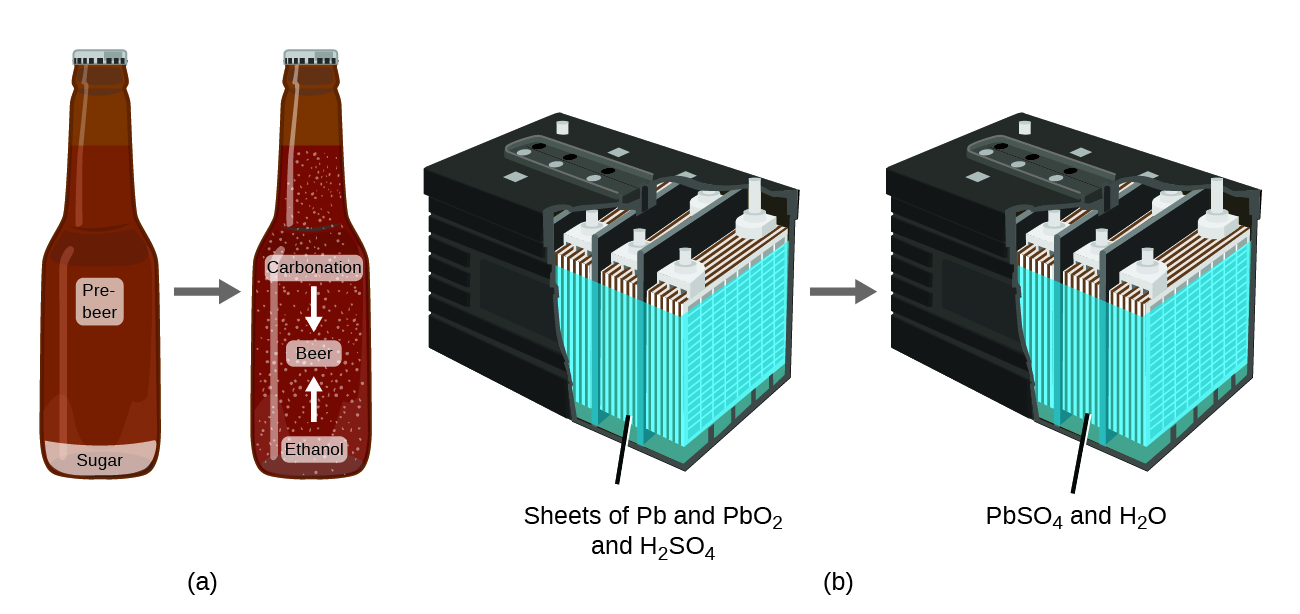
Although this conservation law holds true for all conversions of matter, convincing examples are few and far between because, outside of the controlled conditions in a laboratory, we seldom collect all of the material that is produced during a particular conversion. For example, when you eat, digest, and assimilate food, all of the matter in the original food is preserved. But because some of the matter is incorporated into your body, and much is excreted as various types of waste, it is challenging to verify by measurement.
An atom is the smallest particle of an element that has the properties of that element and can enter into a chemical combination. Consider the element gold, for example. Imagine cutting a gold nugget in half, then cutting one of the halves in half, and repeating this process until a piece of gold remained that was so small that it could not be cut in half (regardless of how tiny your knife may be). This minimally sized piece of gold is an atom (from the Greek atomos , meaning “indivisible”) ( [link] ). This atom would no longer be gold if it were divided any further.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?