| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Ions of the lighter d -block elements, such as Cr 3+ , Fe 3+ , and Co 2+ , form colorful hydrated ions that are stable in water. However, ions in the period just below these (Mo 3+ , Ru 3+ , and Ir 2+ ) are unstable and react readily with oxygen from the air. The majority of simple, water-stable ions formed by the heavier d -block elements are oxyanions such as and
Ruthenium, osmium, rhodium, iridium, palladium, and platinum are the platinum metals . With difficulty, they form simple cations that are stable in water, and, unlike the earlier elements in the second and third transition series, they do not form stable oxyanions.
Both the d - and f -block elements react with nonmetals to form binary compounds; heating is often required. These elements react with halogens to form a variety of halides ranging in oxidation state from 1+ to 6+. On heating, oxygen reacts with all of the transition elements except palladium, platinum, silver, and gold. The oxides of these latter metals can be formed using other reactants, but they decompose upon heating. The f -block elements, the elements of group 3, and the elements of the first transition series except copper react with aqueous solutions of acids, forming hydrogen gas and solutions of the corresponding salts.
Transition metals can form compounds with a wide range of oxidation states. Some of the observed oxidation states of the elements of the first transition series are shown in [link] . As we move from left to right across the first transition series, we see that the number of common oxidation states increases at first to a maximum towards the middle of the table, then decreases. The values in the table are typical values; there are other known values, and it is possible to synthesize new additions. For example, in 2014, researchers were successful in synthesizing a new oxidation state of iridium (9+).
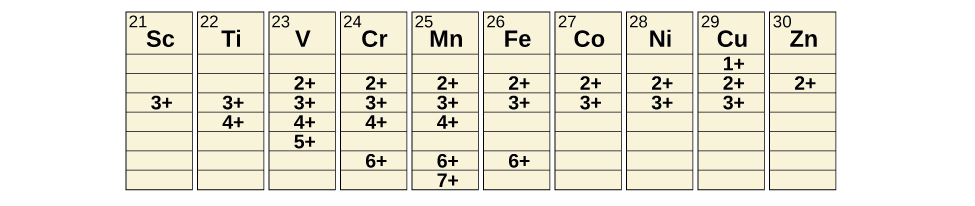
For the elements scandium through manganese (the first half of the first transition series), the highest oxidation state corresponds to the loss of all of the electrons in both the s and d orbitals of their valence shells. The titanium(IV) ion, for example, is formed when the titanium atom loses its two 3 d and two 4 s electrons. These highest oxidation states are the most stable forms of scandium, titanium, and vanadium. However, it is not possible to continue to remove all of the valence electrons from metals as we continue through the series. Iron is known to form oxidation states from 2+ to 6+, with iron(II) and iron(III) being the most common. Most of the elements of the first transition series form ions with a charge of 2+ or 3+ that are stable in water, although those of the early members of the series can be readily oxidized by air.
The elements of the second and third transition series generally are more stable in higher oxidation states than are the elements of the first series. In general, the atomic radius increases down a group, which leads to the ions of the second and third series being larger than are those in the first series. Removing electrons from orbitals that are located farther from the nucleus is easier than removing electrons close to the nucleus. For example, molybdenum and tungsten, members of group 6, are limited mostly to an oxidation state of 6+ in aqueous solution. Chromium, the lightest member of the group, forms stable Cr 3+ ions in water and, in the absence of air, less stable Cr 2+ ions. The sulfide with the highest oxidation state for chromium is Cr 2 S 3 , which contains the Cr 3+ ion. Molybdenum and tungsten form sulfides in which the metals exhibit oxidation states of 4+ and 6+.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?