| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| Source of Innovation | Definition | Examples of Innovation |
| Technical breakthrough | Innovation that results from technical development. | MP3 players; GPS navigation system; Wireless Internet service |
| Non-technical idea development | Finding niche markets without making radical changes to the basic product category. Does not rely on new technology. | ‘Build a bear workshop;’ Frozen yogurt stores |
| Idea from outer environment | Importing ideas from other cultures, places, and settings | IKEA in the US; Yoga or Taekwondo in Western nations |
| Serendipity | Innovation through an accident, when looking for something else | X-rays; Penicillin |
| Purposeful development | Innovation that derives from heavy investment, once strong demand is recognized | Prescription drugs; Pencils with erasers |
It is also possible to create a new business model. Wal-Mart is a good example here, as the retailer applies the philosophy of low prices and cost cutting to every aspect of its operations, including logistics, employee compensation, managerial philosophy, packaging, merchandising, negotiations with suppliers, and so forth. This manner of innovation is discussed in more detail in the section which follows, “Product Categories.”
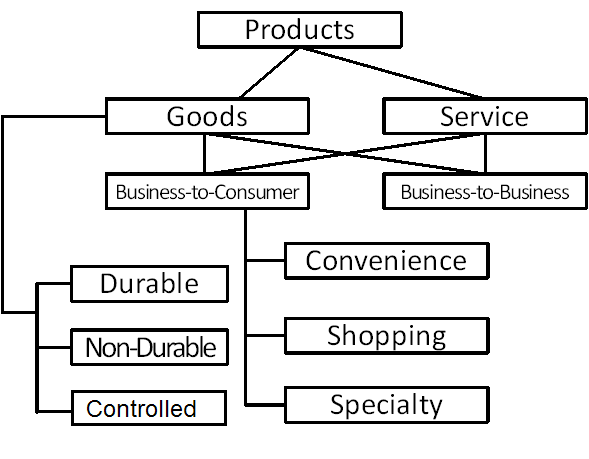
There are a number of ways to classify products (see [link] and [link] ). For instance, a product can be classified by durability and tangibility. Packaged goods are tangible and are consumed in one or a few uses, such as in the case of beer, soap, or fuel. Durable goods are tangible and survive many uses. Consumer examples include furniture, TVs, computers, clothing and automobiles. According to one convention, a durable good lasts more than one year. Non-durable goods are tangible, but they provide benefits for a short time. Good examples include: gum, shaving cream, gas, batteries, and cosmetics. There are also controlled goods which are often restricted by government action, due to their potential danger or addictive nature. Good examples include: cigarettes, alcohol, tobacco, firearms, and even some over-the-counter drugs.
Business-to-business (B2B) products refer to goods bought by individuals or organizations for further processing or for use in doing business. Examples in B2B include: buildings, flour purchased by a commercial baker, crude oil, steel for automobile manufacture, insurance policies for company buildings, and business consulting services. Business-to-customer (B2C) products refer to goods that individual customers purchase for personal and family use, such as passenger cars, hairdryers, TVs, medical insurance policies, and carpet cleaning services for the home.
Convenience products are products that consumers want to purchase frequently, immediately, and with a minimum of effort. Examples here include: soft drinks, cigarettes, fast foods, newspapers, public transportation and candy bars. Shopping goods are purchased only after consumers make comparisons with competing goods based on such attributes as price, quality, style, or color. Examples in this category include: MP3 players, passenger cars, clothing, furniture, and houses. Specialty products are products with unique characters. Buyers often prize such goods and make a special effort to obtain them. Examples in this group include collectable items, engagement rings, vacation homes, yachts, art works, luxury cars, and special concert tickets.
| Category Name | Definition | Example |
| Good | A tangible physical entity | Table, electronics, soda, candy bar |
| Service | An intangible result of the application of human and mechanical efforts to people or objects. | Haircut, dry-cleaning, gardening |
| Durable | Products that provide benefit for a long time and are not used up when used once. | Automobile, house, machines |
| Non-durable | Products that provide benefit for a short time. | Milk, laundry detergents, tissue paper |
| Controlled Goods | Products that need to be regulated due to their potential danger or addictive potential. | Tobacco, alcohol, firearms, pharmaceuticals |
| Business-to-business | Goods bought by individuals or organizations for further processing or for use in doing business. | plastics for a car manufacturer, insurance plan for plants |
| Consumer | The goods individual consumers purchase for personal or family use. | Canned soup, medical insurance |
| Convenience | Products that consumers want to purchase frequently, immediately, and with a minimum of effort. | Chewing gum, beer, cigarettes, fast food |
| Shopping | Products purchased only after the consumer has made comparisons with competing goods on such bases as price, quality, style, or color. | TV, automobile, house |
| Specialty | Products with unique characterizations that cause the buyer to prize them and make a special effort to obtain them. | Luxury sports car, jewelry, |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Business fundamentals' conversation and receive update notifications?