| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
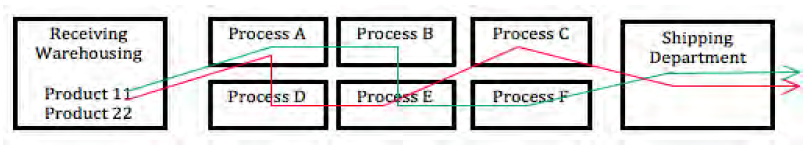
Intermittent processes are also used in manufacturing operations where a wide variety of products are manufactured, or where products are made to customer specifications. Equipment and labor can be organized into departments such as drilling, punch press, lathe, machining, painting, heat treating, molding, etc. Raw materials and components are routed through the facility according to the type and order of manufacturing activities necessary to produce the finished items. [link] illustrates how two different products, “A63” and “B5” make their way through an intermittent process layout.
Repetitive processes are used to produce identical or very similar products in high volumes. Equipment and labor are organized in a line flow arrangement to meet very specific customer or product processing requirements. Examples include assembly lines that produce products such as computers, cars, hamburgers, automatic car washes, and cafeteria lines. In all of these cases, the products or customers follow the same production steps to produce a standardized outcome. Since the production requirements to produce each unit of output are so well understood, there are many opportunities to achieve high levels of efficiency in repetitive process environments. Efficiency is a key goal in repetitive process environments. Investments in automation and technology are financially justified because the high volume of production spreads out the investment cost over more items/customers.
A paper mill is a good example of a repetitive process. The manufacturing requirements are well-understood, capital investment in automation is high, and production volume is extremely high to keep unit production costs as low as possible.
[link] represents an example of a repetitive process for producing a product such as a small appliance, where raw materials and components are assembled to each unit at different stages of production. The units flow through the facility in a uniform pattern until they are completed and shipped to the customer.

The two main differences between the intermittent and repetitive processes are product variety and product volume.
Intermittent processes are very flexible in meeting the individual requirements of different products or customers, but they tend to be very inefficient, with high amounts of waiting time, work in process inventories, and space requirements. Repetitive processes are very efficient at reducing unit production costs, waiting time, and inventories, but they are not very flexible in accommodating high product/customer variety. A compromise solution is the cellular process layout that captures the advantages of both intermittent and repetitive processes.
A cellular process arranges dissimilar machines and equipment together in a line that is dedicated to producing a specific family of products that have similar processing requirements. By setting up multiple dedicated cells, the facility can efficiently produce a wide variety of products ( [link] ). Since the products within a family have similar production requirements, equipment setup times, inventories, and lot sizes can be kept to a minimum. The cellular approach allows each product to be sent through the manufacturing process one piece at a time, according to the immediate set of customer orders. It provides workers the flexibility to change a product or customize it in some way in response to specific customer requirements. The cells are usually arranged in a U shape. This enables one worker to view multiple machines simultaneously and puts all machines within easy reaching distance. Cellular processes minimize cycle times and enable the organization to maintain higher levels of product volumes, variety, and customization.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Business fundamentals' conversation and receive update notifications?