| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Concepts of animal population dynamics can be applied to human population growth. Humans are not unique in their ability to alter their environment. For example, beaver dams alter the stream environment where they are built. Humans, however, have the ability to alter their environment to increase its carrying capacity, sometimes to the detriment of other species. Earth’s human population and their use of resources are growing rapidly, to the extent that some worry about the ability of Earth’s environment to sustain its human population. Long-term exponential growth carries with it the potential risks of famine, disease, and large-scale death, as well as social consequences of crowding such as increased crime.
Human technology and particularly our harnessing of the energy contained in fossil fuels have caused unprecedented changes to Earth’s environment, altering ecosystems to the point where some may be in danger of collapse. Changes on a global scale including depletion of the ozone layer, desertification and topsoil loss, and global climate change are caused by human activities.
The world’s human population is presently growing exponentially ( [link] ).
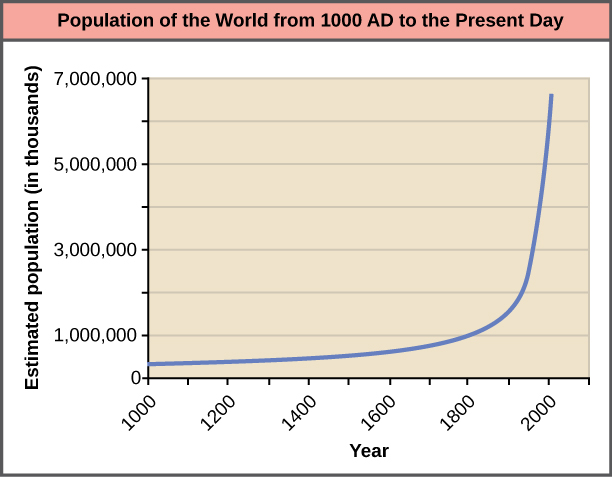
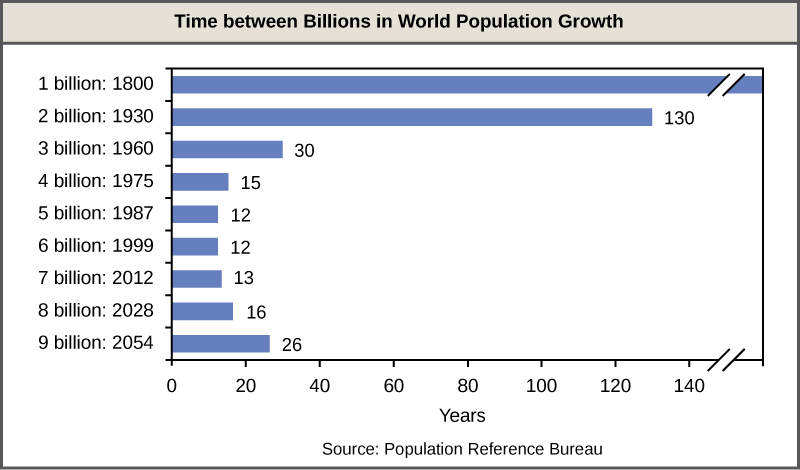
A consequence of exponential growth rate is that the time that it takes to add a particular number of humans to the population is becoming shorter. [link] shows that 123 years were necessary to add 1 billion humans between 1804 and 1930, but it only took 24 years to add the two billion people between 1975 and 1999. This acceleration in growth rate will likely begin to decrease in the coming decades. Despite this, the population will continue to increase and the threat of overpopulation remains, particularly because the damage caused to ecosystems and biodiversity is lowering the human carrying capacity of the planet.
Click through this interactive view of how human populations have changed over time.
Humans are unique in their ability to alter their environment in myriad ways. This ability is responsible for human population growth because it resets the carrying capacity and overcomes density-dependent growth regulation. Much of this ability is related to human intelligence, society, and communication. Humans construct shelters to protect themselves from the elements and have developed agriculture and domesticated animals to increase their food supplies. In addition, humans use language to communicate this technology to new generations, allowing them to improve upon previous accomplishments.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?