| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
You have learned about the catabolism of glucose, which provides energy to living cells. But living things consume more than glucose for food. How does a turkey sandwich end up as ATP in your cells? This happens because all of the catabolic pathways for carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids eventually connect into glycolysis and the citric acid cycle pathways (see [link] ). Metabolic pathways should be thought of as porous—that is, substances enter from other pathways, and intermediates leave for other pathways. These pathways are not closed systems. Many of the substrates, intermediates, and products in a particular pathway are reactants in other pathways.
Glycogen, a polymer of glucose, is an energy storage molecule in animals. When there is adequate ATP present, excess glucose is shunted into glycogen for storage. Glycogen is made and stored in both liver and muscle. The glycogen will be hydrolyzed into glucose monomers (G-1-P) if blood sugar levels drop. The presence of glycogen as a source of glucose allows ATP to be produced for a longer period of time during exercise. Glycogen is broken down into G-1-P and converted into G-6-P in both muscle and liver cells, and this product enters the glycolytic pathway.
Sucrose is a disaccharide with a molecule of glucose and a molecule of fructose bonded together with a glycosidic linkage. Fructose is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galactose (which is part of the milk sugar, the disaccharide lactose), which are absorbed directly into the bloodstream during digestion. The catabolism of both fructose and galactose produces the same number of ATP molecules as glucose.
Proteins are hydrolyzed by a variety of enzymes in cells. Most of the time, the amino acids are recycled into the synthesis of new proteins. If there are excess amino acids, however, or if the body is in a state of starvation, some amino acids will be shunted into the pathways of glucose catabolism ( [link] ). Each amino acid must have its amino group removed prior to entry into these pathways. The amino group is converted into ammonia. In mammals, the liver synthesizes urea from two ammonia molecules and a carbon dioxide molecule. Thus, urea is the principal waste product in mammals produced from the nitrogen originating in amino acids, and it leaves the body in urine.
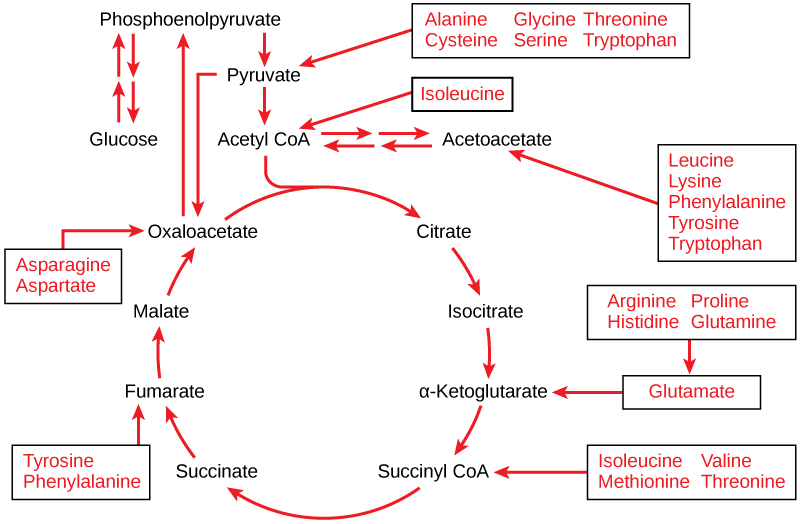
The lipids that are connected to the glucose pathways are cholesterol and triglycerides. Cholesterol is a lipid that contributes to cell membrane flexibility and is a precursor of steroid hormones. The synthesis of cholesterol starts with acetyl groups and proceeds in only one direction. The process cannot be reversed.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?